Complement C3d enables cell-mediated immunity capable of distinguishing spontaneously transformed from nontransformed cells
- PMID: 39693340
- PMCID: PMC11670236
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2405824121
Complement C3d enables cell-mediated immunity capable of distinguishing spontaneously transformed from nontransformed cells
Abstract
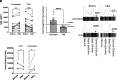
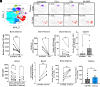
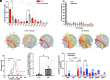
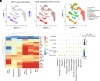
Immune surveillance depends in part on the recognition of peptide variants by T cell antigen receptors. Given that both normal B cells and malignant B cells accumulate mutations we chose a murine model of multiple myeloma to test conditions to induce cell-mediated immunity targeting malignant plasma cell (PC) clones but sparing of normal PCs. Revealing a previously unknown function for intracellular C3d, we found that C3d engaged T cell responses against malignant PC in the bone marrow of mice that had developed multiple myeloma spontaneously. Our results show that C3d internalized by cells augments immune surveillance by several mechanisms. In one, C3d induces a master transcription regulator, E2f1, to increase the expression of long noncoding (lnc) RNAs, to generate peptides for MHC-I presentation, and increase MHC-I expression. In another, C3d increases expression of RNAs encoding ribosomal proteins linked to processing of defective ribosomal products that arise from noncanonical translation and known to promote immunosurveillance. Cancer cells are uniquely susceptible to increased expression and presentation of mutant peptides given the extent of protein misfolding and accumulation of somatic mutations. Accordingly, although C3d can be internalized by any cell, C3d preferentially targets malignant clones by evoking specific T cell-mediated immunity and sparing most nontransformed polyclonal B cells and PC with lower mutation loads. Malignant PC deletion was blocked by cyclosporin or by CD8 depletion confirming that endogenous T cells mediated malignant clone clearance. Besides the potential for therapeutic application our results highlight how intracellular C3d modifies cellular metabolism to augment immune surveillance.
Keywords: Cell-mediated immunity; Complement 3 d; immune-surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:C3d Immunotherapies” Patent submitted on 04/18/2023 “C3d cellular and acellular vaccines for the prevention and treatment of cancer.” PCT NO:US-01/34733-converted and awarded in 2021.
Figures


Update of
-
Complement C3d enables protective immunity capable of distinguishing spontaneously transformed from non-transformed cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 31:2024.07.31.606044. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.31.606044. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Dec 24;121(52):e2405824121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2405824121. PMID: 39211250 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

