The Depth Estimation and Visualization of Dermatological Lesions: Development and Usability Study
- PMID: 39693616
- PMCID: PMC11694055
- DOI: 10.2196/59839
The Depth Estimation and Visualization of Dermatological Lesions: Development and Usability Study
Abstract
Background: Thus far, considerable research has been focused on classifying a lesion as benign or malignant. However, there is a requirement for quick depth estimation of a lesion for the accurate clinical staging of the lesion. The lesion could be malignant and quickly grow beneath the skin. While biopsy slides provide clear information on lesion depth, it is an emerging domain to find quick and noninvasive methods to estimate depth, particularly based on 2D images.
Objective: This study proposes a novel methodology for the depth estimation and visualization of skin lesions. Current diagnostic methods are approximate in determining how much a lesion may have proliferated within the skin. Using color gradients and depth maps, this method will give us a definite estimate and visualization procedure for lesions and other skin issues. We aim to generate 3D holograms of the lesion depth such that dermatologists can better diagnose melanoma.
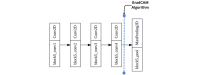
Methods: We started by performing classification using a convolutional neural network (CNN), followed by using explainable artificial intelligence to localize the image features responsible for the CNN output. We used the gradient class activation map approach to perform localization of the lesion from the rest of the image. We applied computer graphics for depth estimation and developing the 3D structure of the lesion. We used the depth from defocus method for depth estimation from single images and Gabor filters for volumetric representation of the depth map. Our novel method, called red spot analysis, measures the degree of infection based on how a conical hologram is constructed. We collaborated with a dermatologist to analyze the 3D hologram output and received feedback on how this method can be introduced to clinical implementation.
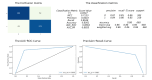
Results: The neural model plus the explainable artificial intelligence algorithm achieved an accuracy of 86% in classifying the lesions correctly as benign or malignant. For the entire pipeline, we mapped the benign and malignant cases to their conical representations. We received exceedingly positive feedback while pitching this idea at the King Edward Memorial Institute in India. Dermatologists considered this a potentially useful tool in the depth estimation of lesions. We received a number of ideas for evaluating the technique before it can be introduced to the clinical scene.
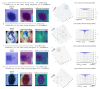
Conclusions: When we map the CNN outputs (benign or malignant) to the corresponding hologram, we observe that a malignant lesion has a higher concentration of red spots (infection) in the upper and deeper portions of the skin, and that the malignant cases have deeper conical sections when compared with the benign cases. This proves that the qualitative results map with the initial classification performed by the neural model. The positive feedback provided by the dermatologist suggests that the qualitative conclusion of the method is sufficient.
Keywords: ML; MR; XAI; artificial intelligence; computer graphics; computer vision; explainable AI; machine learning; mixed reality; neural networks; red spot analysis; visualization.
©Pranav Parekh, Richard Oyeleke, Tejas Vishwanath. Originally published in JMIR Dermatology (http://derma.jmir.org), 18.12.2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic performance of augmented intelligence with 2D and 3D total body photography and convolutional neural networks in a high-risk population for melanoma under real-world conditions: A new era of skin cancer screening?Eur J Cancer. 2023 Sep;190:112954. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.112954. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Eur J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37453242
-
Dermatologist versus artificial intelligence confidence in dermoscopy diagnosis: Complementary information that may affect decision-making.Exp Dermatol. 2023 Oct;32(10):1744-1751. doi: 10.1111/exd.14892. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Exp Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37534916
-
Unveiling the power of convolutional neural networks in melanoma diagnosis.Eur J Dermatol. 2023 Oct 1;33(5):495-505. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2023.4559. Eur J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 38297925
-
Towards real-time photorealistic 3D holography with deep neural networks.Nature. 2021 Mar;591(7849):234-239. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03152-0. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33692557
-
Skin cancer classification via convolutional neural networks: systematic review of studies involving human experts.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Oct;156:202-216. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.06.049. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34509059
References
-
- Satheesha TY, Satyanarayana D, Prasad MNG, Dhruve KD. Melanoma is skin deep: a 3D reconstruction technique for computerized dermoscopic skin lesion classification. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2017;5:4300117. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2017.2648797. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/28512610 4300117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhati P, Singhal M. Early stage detection and classification of melanoma. 2015 Communication, Control and Intelligent Systems (CCIS); November 7-8, 2015; Mathura, India. 2015. pp. 181–185. - DOI
-
- Kłosok M, Chlebus M. Towards Better Understanding of Complex Machine Learning Models Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) - Case of Credit Scoring Modelling. Warszawa, Poland: Faculty of Economic Sciences, University of Warsaw; 2020.
-
- Sahija D. Critical review of mixed reality integration with medical devices for patient care. IJIRMF. 2022;8(1):1–7.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

