Palmitoylation and regulation of potassium-dependent sodium/calcium exchangers (NCKX)
- PMID: 39693635
- PMCID: PMC12096950
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20241051
Palmitoylation and regulation of potassium-dependent sodium/calcium exchangers (NCKX)
Abstract
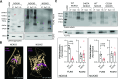
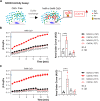
Cellular Ca2+ homeostasis is critical for normal cell physiology and is regulated by several mechanisms. Two major players in intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis in multiple tissues belong to the SLC8 (Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCXs); NCX1-3) and SLC24 (K+ dependent Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCKXs); NCKX1-5) families. It has been established that NCXs and NCKX4 are palmitoylated, and that palmitoylation promotes NCX1 inactivation. However, there is still little known about NCKXs' palmitoylation. We found that (1) NCKX3 and NCKX5, but not NCKX1, are palmitoylated, (2) Cys to Ala mutation at position 467 for NCXK3 and 325 for NCKX5 notably diminished palmitoylation and (3) reduced palmitoylation enhanced NCKX3 activity. Our findings bring novel insights into NCKX1, NCKX3 and NCKX5 palmitoylation and establish palmitoylation as an endogenous regulator of NCKX3 activity, paving the way for investigations evaluating the role of palmitoylation in NCKX3 function in health and disease.
Keywords: Ca2+homeostasis; NCKX; Solute Carrier (SLC) proteins; palmitoylation.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

