Thermodynamic role of receptor phosphorylation barcode in cannabinoid receptor desensitization
- PMID: 39693934
- PMCID: PMC11706802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.151100
Thermodynamic role of receptor phosphorylation barcode in cannabinoid receptor desensitization
Abstract
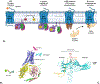
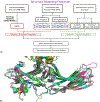
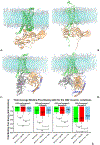
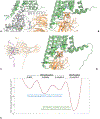
The endocannabinoid signaling system is comprised of CB1 and CB2 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). CB2 receptor subtype is predominantly expressed in the immune cells and signals through its transducer proteins (Gi protein and β-arrestin-2). Arrestins are signaling proteins that bind to many GPCRs after receptor phosphorylation to terminate G protein signaling (desensitization) and to initiate specific G protein-independent arrestin-mediated signaling pathways via a "phosphorylation barcode", that captures sequence patterns of phosphorylated Ser/Thr residues in the receptor's intracellular domains and can lead to different signaling effects. The structural basis for how arrestins and G proteins compete with the receptor for biased signaling and how different barcodes lead to different signaling profiles is not well understood as there is a lack of phosphorylated receptor structures in complex with arrestins. In this work, structural models of β-arrestin-2 were built in complex with the phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of the CB2 receptor. The complex structures were relaxed in the lipid bilayer environment with molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and analyzed structurally and thermodynamically. The β-arrestin-2 complex with the phosphorylated receptor was more stable than the non-phosphorylated one, highlighting the thermodynamic role of the receptor phosphorylation. It was also more stable than any of the G protein complexes with CB2 suggesting that phosphorylation signals receptor desensitization (end of G protein signaling) and arrest of the receptor by arrestins. These models are beginning to provide the thermodynamic landscape of CB2 signaling, which can help bias signaling towards therapeutically beneficial pathways in drug discovery applications.
Keywords: Endocannabinoid system; GPCRs; Molecular dynamics; Phosphopeptide; Signaling complexes.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Ravinder Abrol reports financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health. Ravinder Abrol reports a relationship with Phyteau Inc. that includes: equity or stocks. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protocol to Study β-Arrestin Recruitment by CB1 and CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1412:103-11. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3539-0_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27245896
-
G-protein receptor kinase 5 regulates the cannabinoid receptor 2-induced up-regulation of serotonin 2A receptors.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 31;288(22):15712-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.454843. Epub 2013 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23592773 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating the interactions between the cannabinoid CB2 receptor and its regulatory effectors; β-arrestins and GPCR kinases.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 May;179(10):2223-2239. doi: 10.1111/bph.15748. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34811740
-
β-arrestins and G protein-coupled receptor trafficking.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;219:173-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41199-1_9. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24292830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G protein-coupled receptor interactions with arrestins and GPCR kinases: The unresolved issue of signal bias.J Biol Chem. 2022 Sep;298(9):102279. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102279. Epub 2022 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35863432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li X, Hua T, Vemuri K, Ho JH, Wu Y, Wu L, Popov P, Benchama O, Zvonok N, Locke K, Qu L, Han GW, Iyer MR, Cinar R, Coffey NJ, Wang J, Wu M, Katritch V, Zhao S, Kunos G, Bohn LM, Makriyannis A, Stevens RC, Liu ZJ, Crystal structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB2, Cell 176 (2019) 459–467.e13, 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

