Detection of cardiac amyloidosis using machine learning on routine echocardiographic measurements
- PMID: 39694574
- PMCID: PMC11667434
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2024-002884
Detection of cardiac amyloidosis using machine learning on routine echocardiographic measurements
Abstract
Background: Cardiac amyloidosis (CA) is an underdiagnosed, progressive and lethal disease. Machine learning applied to common measurements derived from routine echocardiogram studies can inform suspicion of CA.
Objectives: Our objectives were to test a random forest (RF) model in detecting CA.
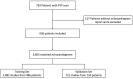
Methods: We used 3603 echocardiogram studies from 636 patients at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center to train an RF model to predict CA from echocardiographic parameters. 231 patients with CA were compared with 405 control patients with negative pyrophosphate scans or clinical diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 19 common echocardiographic measurements from echocardiogram reports were used as input into the RF model. Data was split by patient into a training data set of 2882 studies from 486 patients and a test data set of 721 studies from 150 patients. The performance of the model was evaluated by area under the receiver operative curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value (PPV) on the test data set.
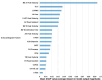
Results: The RF model identified CA with an AUC of 0.84, sensitivity of 0.82, specificity of 0.73 and PPV of 0.76. Some echocardiographic measurements had high missingness, suggesting gaps in measurement in routine clinical practice. Features that were large contributors to the model included mitral A-wave velocity, global longitudinal strain (GLS), left ventricle posterior wall diameter end diastolic (LVPWd) and left atrial area.
Conclusion: Machine learning on echocardiographic parameters can detect patients with CA with accuracy. Our model identified several features that were major contributors towards identifying CA including GLS, mitral A peak velocity and LVPWd. Further study is needed to evaluate its external validity and application in clinical settings.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy, Restrictive; Diagnostic Imaging; Echocardiography.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: This research was funded by Alexion. CD and PR are employees of Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease at the time of publication and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. DO reports consulting fees from Ultromics, InVision, Echo IQ, Pfizer and research grants from NIH NHLBI and Alexion. All other authors report no disclosures to report.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
