Impact of postpartum exercise on pelvic floor disorders and diastasis recti abdominis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39694630
- PMCID: PMC12013572
- DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2024-108619
Impact of postpartum exercise on pelvic floor disorders and diastasis recti abdominis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To examine the effect of exercise during the first year postpartum on pelvic floor disorders and diastasis recti abdominis.
Design: Systematic review with random effects meta-analysis.
Data sources: MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, SPORTDiscuss, Evidence-Based Medicine Reviews (Ovid), Scopus, Web of Science and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched until 12 January 2024.
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: Studies of all designs (except case studies) and languages were included if they contained information on the Population (individuals in the first year postpartum), Intervention (subjective or objective measures of frequency, intensity, duration, volume or type of exercise alone ('exercise-only') or in combination with other intervention (eg, biofeedback; 'exercise+co-intervention')), Comparator (no exercise or different exercise measures) and Outcome (symptom severity and risk of urinary incontinence, anal incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, diastasis recti abdominis and sexual function).
Results: 65 studies (n=21 334 participants) from 24 countries were included. 'Moderate' certainty of evidence revealed that pelvic floor muscle training reduced the odds of urinary incontinence by 37% (seven randomised controlled trials (RCTs), n=1930; OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.97, I2 72%) and pelvic organ prolapse by 56% (one RCT, n=123; OR 0.44, 95% CI 0.21 to 0.91) compared with control groups. 'Low' certainty of evidence showed a greater reduction in inter-rectus distance measured at rest and during a head lift following abdominal muscle training compared with no exercise. Evidence on the effect of exercise on the risk of anal incontinence and diastasis recti abdominis, as well as the severity of anal incontinence, urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse and sexual function, is limited.
Conclusion: Evidence supports the effectiveness of postpartum pelvic floor muscle training in reducing the odds of urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse and postpartum abdominal exercise training in reducing inter-rectus distance.
Prospero registration number: CRD42022359282.
Keywords: exercise; gynaecology; pelvic floor; urinary incontinence, stress; women.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


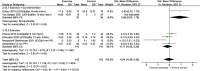




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
