Structural mechanism of CB1R binding to peripheral and biased inverse agonists
- PMID: 39695122
- PMCID: PMC11655885
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54206-0
Structural mechanism of CB1R binding to peripheral and biased inverse agonists
Abstract
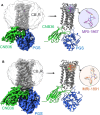
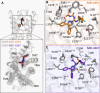
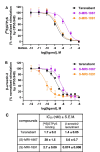
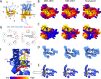
The cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R) regulates synaptic transmission in the central nervous system, but also has important roles in the peripheral organs controlling cellular metabolism. While earlier generations of brain penetrant CB1R antagonists advanced to the clinic for their effective treatment of obesity, such molecules were ultimately shown to exhibit negative effects on central reward pathways that thwarted their further therapeutic development. The peripherally restricted CB1R inverse agonists MRI-1867 and MRI-1891 represent a new generation of compounds that retain the metabolic benefits of CB1R inhibitors while sparing the negative psychiatric effects. To understand the mechanism of binding and inhibition of CB1R by peripherally restricted antagonists, we developed a nanobody/fusion protein strategy for high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination of the GPCR inactive state, and used this method to determine structures of CB1R bound to either MRI-1867 or MRI-1891. These structures reveal how these compounds retain high affinity and specificity for CB1R's hydrophobic orthosteric site despite incorporating polar functionalities that lead to peripheral restriction. Further, the structure of the MRI-1891 complex along with accompanying molecular dynamics simulations shows how differential engagement with transmembrane helices and the proximal N-terminus can propagate through the receptor to contribute to biased inhibition of β-arrestin signaling.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mechoulam, R. & Parker, L. A. The endocannabinoid system and the brain. Annu Rev. Psychol.64, 21–47 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Gaoni, Y. & Mechoulam, R. Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J Am Chem Soc. (1964). - PubMed
-
- Mackie, K. Cannabinoid receptors as therapeutic targets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.46, 101–122 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Ramesh, K. & Rosenbaum, D. M. Molecular basis for ligand modulation of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol.179, 3487–3495 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

