CUL4B protects kidneys from acute injury by restraining p53/PAI-1 signaling
- PMID: 39695153
- PMCID: PMC11655551
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-07299-w
CUL4B protects kidneys from acute injury by restraining p53/PAI-1 signaling
Abstract
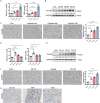
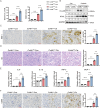
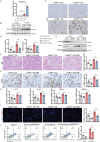
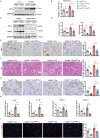
Acute kidney injury (AKI) caused by nephrotoxins, ischemia reperfusion (IR) or sepsis is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Unveiling new mechanisms underlying AKI can help develop new therapeutic strategy. Cullin 4B (CUL4B) is a scaffold protein in the CUL4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL4B) complex. Here, we demonstrate that CUL4B can protect kidneys from acute injury induced by cisplatin and IR. CUL4B is upregulated in mouse tubular epithelial cells (TECs) after cisplatin treatment or IR. Loss of CUL4B in kidneys exacerbates renal injury, inflammation, and apoptosis of TECs caused by cisplatin and IR. Transcriptome analysis reveals that Cul4b deficiency enhances injury-induced PAI-1 expression. CUL4B suppresses PAI-1 expression by promoting polyubiquitination and degradation of p53. Inhibition of either PAI-1 or p53 can prevent the aggravated renal injury and inflammation caused by loss of CUL4B. Our work has identified the kidney-protective role of CUL4B against acute injury.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, Ronco C, Zarbock A, Anders HJ. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:52. - PubMed
-
- Ronco C, Bellomo R, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury. Lancet. 2019;394:1949–64. - PubMed
-
- Hu H, Yang Y, Ji Q, Zhao W, Jiang B, Liu R, et al. CRL4B catalyzes H2AK119 monoubiquitination and coordinates with PRC2 to promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:781–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

