Gestational weight gain during pregnancy is the risk factor for Omicron infection: a retrospective case-control study
- PMID: 39695418
- PMCID: PMC11657632
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-024-07025-6
Gestational weight gain during pregnancy is the risk factor for Omicron infection: a retrospective case-control study
Abstract
Background: It remains unclear whether gestational weight gain (GWG) during pregnancy is associated with Omicron infection in pregnant women.
Objective: To investigate whether gestational weight gain during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of Omicron infection.
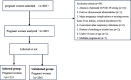
Methods: This is a retrospective case-control study of pregnant women from The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University from December 1 to 31, 2022. Pregnant women infected with Omicron were compared to those uninfected using chi-square statistics for categorical variables and t-tests or ANOVA for continuous variables. Multivariable logistic regression, along with subgroup analyses, was used to investigate the association between gestational weight gain during pregnancy and Omicron infection.
Results: Our study included 369 pregnant women who met the eligibility criteria. The proportion of pregnant women in the term, infected and uninfected with Omicron was 113(30.6%) and 256(69.4%). Classified pregnant women according to GWG during pregnancy, GWG during pregnancy above IOM was significantly associated with an increased risk of Omicron infection (P = 0.006). After adjusting for demographic factors and pregnancy complications, this association was particularly notable (OR = 2.55, 95%CI = 1.35-4.85, P = 0.004). Classified pregnant women according to pregestational BMI, in normal-weight pregnant women, GWG during pregnancy above IOM was significantly associated with an increased risk of Omicron infection (P = 0.01). After adjusting for demographic factors and pregnancy complications, this association was particularly notable (OR = 2.56, 95%CI = 1.24-5.31, P = 0.01).
Conclusion: Among women with normal weight, gestational weight gain during pregnancy above IOM was an independent risk factor for Omicron infection.
Keywords: Gestational weight gain; IOM; Omicron; Risk factor; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study received approval from the Ethics Review Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, with the assigned approval number II2023-094–01 by the China University of China. This study pertains to anonymous retrospective queue research conducted on patients, thereby fulfilling the criteria for exemption from informed consent. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
References
-
- Katz D, Bateman BT, Kjaer K, et al. The Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology Coronavirus Disease 2019 Registry: An Analysis of Outcomes Among Pregnant Women Delivering During the Initial Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Outbreak in the United States. Anesth Analg. 2021;133(2):462–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous