The moderating effect of dietary fiber intake on the association between sleep pattern and liver fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a study from NHANES
- PMID: 39695427
- PMCID: PMC11654364
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-024-03538-8
The moderating effect of dietary fiber intake on the association between sleep pattern and liver fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a study from NHANES
Abstract
Background: Insufficient nocturnal sleep was associated with a higher risk of fibrosis in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Dietary fiber intake may improve the stimulate the secretion of sleep cytokines, inhibit the inflammatory pathway, contribute to regulating sleep disorders and alleviate liver fibrosis. The associations of dietary fiber intake, sleep patterns, with liver fibrosis remain unclear. The study aimed to explore the associations between dietary fiber, sleep, and liver fibrosis, as well as the moderating effect of dietary fiber intake between sleep patterns and liver fibrosis in MASLD patients.
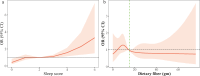
Methods: Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database spanning from 2017 to 2020, a cross-sectional study included participants with MASLD was performed to assess the relationship between sleep patterns, dietary fiber intake, and liver fibrosis. Weighted univariate and multivariate logistic regression models were used to examine the linear connection between sleep pattern, dietary fiber intake, and liver fibrosis. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) method was also performed to describe the nonlinear relationship. A two-part linear regression model was also used to estimate threshold effects. The moderating effect of dietary fiber intake was further investigated in different subgroups. All results were presented as odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: Totally, 1343 MASLD patients were included for final analysis. Among them, 207 (15.41%) have liver fibrosis. Dietary fiber intake did not correlate significantly with sleep pattern in patients with MASLD (Spearman's r = -0.028, P = 0.1678). Poor sleep pattern was related to higher odds of liver fibrosis (OR = 3.23, 95%CI: 1.05-9.90), while dietary fiber intake ≥ 15 gm/day was associated with lower liver fibrosis risk (OR = 0.51, 95%CI: 0.32-0.83). On the association between sleep pattern and liver fibrosis stratified by dietary fiber intake revealed that poor sleep patterns (OR = 15.13, 95%CI: 4.40-52.01) remained associated with increased liver fibrosis risk among individuals with dietary fiber intake < 15 gm/day. No connection was observed between poor sleep patterns and liver fibrosis in MASLD patients with higher dietary fiber intake, with moderate dietary fiber supplementation beneficial in mitigating poor sleep patterns associated with liver fibrosis. The similar findings were also found in patients aged < 50 years old, ≥ 50 years old, females, those with and without CVD groups, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Particularly, dietary fiber intake also moderates the relationship between sleep patterns and liver fibrosis in the F4 stage (OR = 13.26, 95%CI: 4.08-43.11).
Conclusion: Dietary fiber intake affects the relationship between sleep patterns and liver fibrosis in MASLD patients.
Keywords: Dietary fiber intake; Liver fibrosis; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; NHANES; Sleep.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The requirement of ethical approval for this was waived by the Institutional Review Board of Beijing Shunyi Hospital, because the data was accessed from NHANES (a publicly available database). The need for written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board of Beijing Shunyi Hospital due to retrospective nature of the study. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of niacin intake and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: findings from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.BMC Public Health. 2024 Oct 8;24(1):2742. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20161-0. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39379884 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the lymphocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease among US adults: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2017 to 2020.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 23;24(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03565-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39716074 Free PMC article.
-
Total choline intake, liver fibrosis and the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Results from 2017 to 2020 NHANES.Maturitas. 2025 Jan;191:108150. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2024.108150. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Maturitas. 2025. PMID: 39536658
-
Macronutrient Modulation in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-the Molecular Role of Fatty Acids compared with Sugars in Human Metabolism and Disease Progression.Adv Nutr. 2025 Mar;16(3):100375. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2025.100375. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Adv Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39842721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis as a potential connection between schizophrenia and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease - a narrative review.Postep Psychiatr Neurol. 2024 Sep;33(3):178-187. doi: 10.5114/ppn.2024.142136. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Postep Psychiatr Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39678457 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of dietary inflammatory index with liver fibrosis and fatty liver index in a population with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 24;12:1594192. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1594192. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40630170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic Associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1999–e20141. - PubMed
-
- Chan KE, Koh TJL, Tang ASP, Quek J, Yong JN, Tay P, et al. Global prevalence and clinical characteristics of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: a Meta-analysis and systematic review of 10 739 607 individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107:2691–700. - PubMed
-
- Zhang P, Dong X, Zhang W, Wang S, Chen C, Tang J, et al. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and the risk of cardiovascular disease. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2023;47:102063. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical