Apoptotic body based biomimetic hybrid nanovesicles to attenuate cytokine storms for sepsis treatment
- PMID: 39695736
- PMCID: PMC11656764
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-03058-3
Apoptotic body based biomimetic hybrid nanovesicles to attenuate cytokine storms for sepsis treatment
Abstract
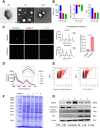
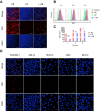
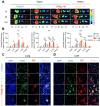
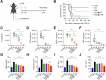
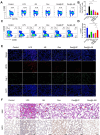
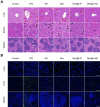
Sepsis is a severe immune response to pathogens that is associated with high mortality rate and a paucity of efficacious treatment options. It is characterized by the hyperactivation of macrophages and the occurrence of cytokine storms. Given the anti-inflammatory properties of M2 macrophages and their derived apoptotic bodies (AB), as well as the specific uptake of these by macrophages, a novel approach was employed to combine AB with artificial liposomes to create apoptotic body based biomimetic hybrid nanovesicles (L-AB). The L-AB effectively inherited "eat me" signaling molecules on the surface of the AB, thereby facilitating their targeted uptake by macrophages in both in vitro and in vivo settings. The administration of L-AB for the delivery of dexamethasone effectively augmented the therapeutic efficacy of the drug, mitigated macrophage hyperactivation and tissue damage in vivo, and consequently enhanced the survival rate of septic mice. Taken together, these findings suggest that the apoptotic body biomimetic nanovesicles may represent a potential drug delivery system capable of specifically targeting macrophages for the treatment of sepsis.
Keywords: Apoptotic body; Biomimetic carrier; Cytokine storm; Macrophages; Sepsis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All the animal experiments were approved by the Experimental Animal Center of HUST. Animal experiments were carried out in compliance with the Guide for the Animals Care and Ethics Committee of HUST, with the assigned [2023] IACUC number (3678). Consent for publication: All authors consent for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Zheng X, Xing YJ, Sun K, Jin HZ, Zhao W, Yu F. Combination therapy with resveratrol and celastrol using folic acid-functionalized exosomes enhances the therapeutic efficacy of sepsis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(27):2301243. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

