A genotype-guided prediction model for the incidence of persistent acute kidney injury following lung transplantation
- PMID: 39696008
- PMCID: PMC11654156
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03871-w
A genotype-guided prediction model for the incidence of persistent acute kidney injury following lung transplantation
Erratum in
-
Correction: A genotype-guided prediction model for the incidence of persistent acute kidney injury following lung transplantation.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Feb 25;26(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04036-z. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40001036 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to develop a nomogram for predicting persistent renal dysfunction in acute kidney injury (AKI) following lung transplantation (LTx).
Method: A total of 229 LTx patients were enrolled, and genotyping for 153 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) was performed. The cohort was randomly divided into training (n = 183) and validation (n = 46) sets in an 8:2 ratio. Statistically significant SNPs identified through pharmacogenomic analysis were combined with clinical factors to construct a comprehensive prediction model for persistent AKI using multivariate logistic regression analysis. Discrimination and calibration analyses were conducted to evaluate the performance of the model. Decision curve analysis was used to assess its clinical utility. Due to the small sample size, bootstrap internal sampling with 500 iterations was adopted for validation to prevent overfitting of the model.
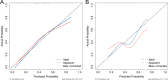
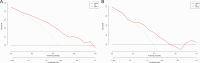
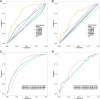
Results: The final nomogram comprised nine predictors, including body mass index, thrombin time, tacrolimus initial concentration, rs757210, rs1799884, rs6887695, rs1494558, rs2069762 and rs2275913. In the training set, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of the nomogram was 0.781 (95%CI: 0.715-0.846), while in the validation set it was 0.698 (95%CI: 0.542-0.855), indicating good model fit. As demonstrated by 500 Bootstrap internal sampling validations, the model has high discrimination and calibration. Additionally, decision curve analysis confirmed its clinical applicability.
Conclusion: This study presents a genotype-guided nomogram that can be used to assess the risk of persistent AKI following LTx and may assist in guiding personalized prevention strategies in clinical practice.
Keywords: Lung transplantation; Persistent acute kidney injury; Prediction model; Tacrolimus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures in this study were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its amendments, and was approved by the Ethics Committee of China-Japan Friendship Hospital in June, 2022 (No. 2022-KY-056-1). A waiver for informed consent was granted by the Ethics Committee of China-Japan Friendship Hospital. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Wajda-Pokrontka M, Nadziakiewicz P, Krauchuk A, et al. Incidence and Perioperative Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury Among Lung Transplant Recipients. Transplant Proc. 2022;54(4):1120–3. - PubMed
-
- Botros M, Jackson K, Singh P, et al. Insights into early postoperative acute kidney injury following lung transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2022;36(4): e14568. - PubMed
-
- Xue J, Wang L, Chen CM, et al. Acute kidney injury influences mortality in lung transplantation. Ren Fail. 2014;36(4):541–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

