Association between ZJU index and gallstones in US adult: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2017-2020
- PMID: 39696023
- PMCID: PMC11654069
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-024-03553-9
Association between ZJU index and gallstones in US adult: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2017-2020
Abstract
Background: Based on triglyceride, body mass index (BMI), alanine aminotransferase/ aspartate aminotransferase ratio, fasting blood glucose, the ZJU index is proven to be a novel and effective parameter for screening NAFLD in Chinese. This study aims to evaluate the correlation between ZJU values and the risk of developing gallstones.
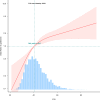
Methods: The data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database during the period from 2017 to 2020 were analyzed in this cross-sectional study. And 6155 participants were included to assess the correlation between the ZJU index and the formation of gallstones through multivariate logistic regression, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, subgroup analysis, and restricted cubic spline regression (RCS) analyses.
Results: In this population-based study, 6155 participants aged 18 years and older were included, among which, 671 had gallstones. Logistic regression and RCS regression analyses indicated a significant positive non-linearly correlation between the ZJU index and the prevalence of gallstones (OR = 1.044, 95% CI: 1.032, 1.056), with an inflection point of 40.6. Subgroup analysis further revealed a stronger correlation between the risk of developing gallstones and the ZJU index in females. ROC analysis indicated that the ZJU index (AUC = 0.653) can serve as a more robust predictor for developing gallstones compared to traditional indices, with a sensitivity of 55.9%, a specificity of 67.1% and a cutoff of 43.4.
Conclusion: This study provides evidence that elevated the ZJU index is correlated with an increased risk of developing gallstones.
Keywords: Body mass index; Gallstones; Insulin resistance; Obesity; ZJU index.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board has approved the implementation of NHANES, and every participant signed informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

