Significant association of miRNA 34a with BRCA1 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: an insight on miRNA regulatory pathways in the Pakistani population
- PMID: 39696052
- PMCID: PMC11657824
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-13259-6
Significant association of miRNA 34a with BRCA1 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: an insight on miRNA regulatory pathways in the Pakistani population
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is among the most aggressive cancers, characterized by high mortality rates. Studies on various cancers across the globe indicate that regulatory miRNAs play a vital role in cellular signaling. However, the expression and interactions of these miRNAs in the Pakistani patients with PDAC is yet to be explored. Here, we aim to investigate a panel of four regulatory miRNAs (miRNA 34a, 30b, 142 and 137) in PDAC and their interaction with selected target proteins in the signaling pathway (KRAS, p53, BRCA1, APC).
Methods: We conducted a study on 109 PDAC patients to analyze the selected miRNAs and protein targets. Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) tumor samples were obtained from the hospital's department of histopathology. After confirmation of diagnosis and appropriate tumor content, tissues were processed for RNA extraction. Based on the acceptable quality and quantity of RNA, 43 samples were proceeded for qRT-PCR. Relative expression of the miRNAs was determined through 2-[ΔΔCt] method. Further, FFPE tumor blocks were used to perform tissue sectioning followed by immunohistochemistry experiments. Stained slides were scored independently by two pathologists according to set criteria.
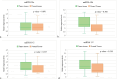
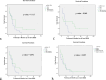
Results: Expression profiles revealed that miRNA 34a, 30b, and 142 showed high expression in approximately 69-70% of cases, while miRNA 137 had a lower high expression frequency (53.4%). Among protein biomarkers, KRAS, BRCA1, and APC were predominantly expressed, with high expression levels observed in 79.1%, 69.8%, and 51.2% of cases, respectively, whereas p53 showed positive expression in only 34.9% of cases. Statistical analysis showed that expression of miRNA 34a was significantly associated with the expression of BRCA1 (p = 0.034). No significant associations were observed for KRAS, p53, or APC with the selected miRNAs. Moreover, the expression of miRNA 34a independently showed significant association with miRNA 30b (p = 0.000) and miRNA 137 (p = 0.001). None of the miRNA showed an association with the overall survival, patient demographics or the clinicopathological characteristics.
Conclusion: Our study highlights a potential bi-directional regulatory relationship between BRCA1 and miRNA 34a, suggesting that miRNA 34a may both respond to and influence BRCA1 activity within cellular signaling pathways. This complex interaction points to a layered regulatory network that could play a crucial role in tumor suppression in PDAC, underscoring the therapeutic potential of targeting this miRNA-protein crosstalk.
Keywords: BRCA1; MiRNA 137; MiRNA 142; MiRNA 30b; MiRNA 34a; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Committee of Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan (2023–6278-25,839). Informed consent was obtained from all the participants. Consent to publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I, Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available from: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today. Accessed 5 Nov 2024.
-
- Jiang Y, Sohal DP. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma management. JCO OP. 2023;19(1):19–32. - PubMed
-
- SEER 2024, https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html. Accessed 5 Nov 2024.
-
- Ali SM, Adnan Y, Ali SA. Pancreatic cancers: a review of studies from Pakistan and comparison with global trends. PJPH. 2021;11(2):120–7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

