Modern tools for optimizing fluid management in dialysis patients: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 39696062
- PMCID: PMC11657891
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03856-9
Modern tools for optimizing fluid management in dialysis patients: a comprehensive review
Abstract
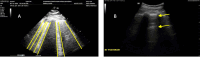
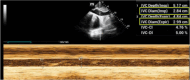
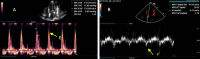
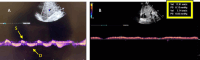
Maintaining optimal fluid balance is crucial for patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis, as both fluid overload and excess removal can lead to poor outcomes. Traditional approaches such as physical exam and chest X-ray have limitations when assessing volume status. This review carefully examines the tools that provide more precise options, including lung ultrasound, echocardiography, Venous Excess Ultrasound (VEXUS), bioimpedance analysis (BIA), and passive leg raise (PLR). We discuss the principles, supporting evidence, and practical uses of these techniques differentiating between static and dynamic methods to evaluate ultrafiltration tolerance. By integrating these modern techniques with clinical judgment, nephrologists can optimize fluid management in dialysis patients. While these tools show promise, further research is needed to establish standardized protocols and evaluate their impact on patient-centered outcomes.
Keywords: Dialysis; Fluid overload; Ultrasound.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

