The evolving role of MRI in the detection of extrathyroidal extension of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39696088
- PMCID: PMC11657418
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-13288-1
The evolving role of MRI in the detection of extrathyroidal extension of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the predominant form of thyroid cancer, and the presence of extrathyroidal extension (ETE) significantly impacts treatment decisions and prognosis. Accurate preoperative detection of ETE remains challenging, highlighting the need to evaluate advanced imaging techniques.This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to investigate the diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in detecting extrathyroidal extension (ETE) among patients diagnosed with papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC).
Method: We conducted a comprehensive search of global databases including PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library, spanning from inception to November 03, 2024. We included studies that utilized preoperative MRI to evaluate the presence of ETE. Quality assessment was carried out using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) standard checklists. Data analysis was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) software version 3. The study protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42024499536).
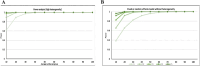
Result: Six studies were included in our final quantitative analysis. The included studies were classified into two groups; the first group focused on evaluating the accuracy of MRI in detecting ETE, while the second group assessed the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC). The accuracy of MRI for overall ETE, minimal ETE (mETE), and gross ETE (gETE) was 81.0% (95% CI: 76.9%-85.6%), 72.9% (95% CI: 66.2%-78.6%), and 83.3% (95% CI: 75.2%-89.1%), respectively. MRI demonstrated a statistically significant difference in detecting gETE compared to mETE (OR = 1.85, 95% CI: 1.01-3.37, P-value = 0.045). Our analysis showed that the ADC of the lesion for b-value 500 is lower in patients with ETE compared to those without ETE (SMD = 0.95, 95% CI: 0.28-1.62, P-value = 0.005).
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that MRI has substantial accuracy in detecting ETE in PTC, especially for gross ETE. This suggests MRI could be a valuable tool in preoperative planning, helping to guide surgical decision-making by more precisely identifying patients at higher risk. However, the limited number of studies underscores the need for further research to confirm MRI's role in routine clinical practice and to refine imaging protocols for more accurate differentiation between minimal and gross ETE.
Keywords: Accuracy; Apparent diffusion coefficient; Extrathyroidal extension; Magnetic resonance imaging; Meta-analysis; Systematic review; Thyroid cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- LeClair K, Bell KJL, Furuya-Kanamori L, Doi SA, Francis DO, Davies L. Evaluation of Gender Inequity in Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis: Differences by Sex in US Thyroid Cancer Incidence Compared With a Meta-analysis of Subclinical Thyroid Cancer Rates at Autopsy. JAMA Intern Med. 2021;181(10):1351–8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

