Norwegian adaptation of the Quality in Psychiatric Care - In-Patient instrument: psychometric properties and factor structure
- PMID: 39696326
- PMCID: PMC11654066
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-11973-2
Norwegian adaptation of the Quality in Psychiatric Care - In-Patient instrument: psychometric properties and factor structure
Abstract
Background: Validated instruments measuring the quality of mental healthcare from patients' perspectives are scarce, and available instruments have been requested. One of the few instruments measuring the quality of care from a patient's perspective is the Swedish Quality in Psychiatric Care-In-Patient (QPC-IP). This cross-sectional study aimed to translate and adapt the QPC-IP instrument for a Norwegian context and assess its psychometric properties.
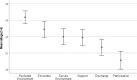
Methods: The QPC-IP was translated and adapted to a Norwegian context using a translation back-translation process model. A total of 169 inpatients from specialised mental health services responded to the questionnaire. The QPC-IP comprises six dimensions: Encounter (eight items), Participation (eight items), Discharge (four items), Support (four items), Secluded Environment (three items), and Secure Environment (three items), totalling 30 items. Confirmatory factor analysis was conducted to assess the instrument's factor structure. Additionally, Cronbach's alpha was used to establish the instrument's internal consistency.
Results: The results indicated that the Norwegian adaptation of the QPC-IP possesses good psychometric properties, including internal consistency, content, and construct validity, as confirmed by the confirmatory factor analysis results. The confirmatory factor analysis demonstrated an adequate fit for the six-factor structure, consistent with the original Swedish instrument.
Conclusions: The QPC-IP is a user-friendly and easily implementable tool that assesses various dimensions of the quality of inpatient mental healthcare from a patient's perspective. Moreover, the Norwegian QPC-IP holds potential for use in comparative, cross-cultural studies within mental healthcare services to monitor the quality of the provided services.
Keywords: Confirmatory factor analysis; Inpatient mental healthcare; Instrument; Patient perspectives; Psychometric properties; Quality of care.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Norwegian Regional Ethical Committee (Ref. 113987). The principles of the Helsinki Declaration were followed regarding integrity, confidentiality, and the voluntary nature of participation [35]. The participants received an envelope containing an invitation letter with information about the study, confidentiality procedures, and the procedure for withdrawing their consent. This information was also provided orally. Participants’ informed consent was implied when questionnaires were completed and submitted. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. The WHO special initiative for mental health (2019–2023): Universal health coverage for mental health. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019 Accessed 10.12.22.
-
- Nylenna M, Bjertnaes ØA, Saunes IS, Lindahl AK. What is Good Quality of Health Care? Professions and professionalism. 2015;5(1). 10.7577/pp.909
-
- Powell RA, Holloway F, Lee J, Sitzia J. Satisfaction research and the uncrowned king: Challenges and future directions. J Ment Health. 2004;13(1):11–20. 10.1080/09638230410001654495. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources