Regulatory effects of statins on CCL2/CCR2 axis in cardiovascular diseases: new insight into pleiotropic effects of statins
- PMID: 39696507
- PMCID: PMC11658147
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-024-00420-y
Regulatory effects of statins on CCL2/CCR2 axis in cardiovascular diseases: new insight into pleiotropic effects of statins
Abstract
Background: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors are well-known medications in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders due to their pleiotropic and lipid-lowering properties. Herein, we reviewed the effects of statins on the CCL2/CCR2 axis.
Method: Scopus and Pubmed databases were systematically searched using the following keywords:" Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA Reductase Inhibitors"," HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors"," Statins", "CCL2, Chemokine", "Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1" and "Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 2". Evidence investigating the role of statin on MCP-1 in CVD was identified and bibliographies were completely evaluated to gather further related studies.
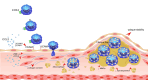
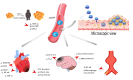
Results: The anti-inflammatory effects of statins on the CCL2/CCR2 pathway have been widely investigated. Despite inconclusive results, a great body of research supports the regulatory roles of statins on this pathway due to their pleiotropic effects. By disrupting the CCL2/CCR2 axis, statins attenuate the infiltration of monocytes and macrophages into the zone of inflammation and hence down-regulate the inflammatory cascades in various CVDs including atherosclerosis, cardiac remodeling, and stroke, among others.
Conclusion: CCL2 plays a major role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disorders. Down-regulation of CCL2 is proposed as one of the pleiotropic properties of statins. However, more investigations are required to elucidate which statin in what dose exerts a more potent effect on CCL2/CCR2 pathway.
Keywords: CCL2; Ischemic heart disease; MCP-1; Statins; Stroke.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lukacs NW. Role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1(2):108–16. 10.1038/35100503. - PubMed
-
- Mahad DJ, Ransohoff RM. The role of MCP-1 (CCL2) and CCR2 in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Semin Immunol. 2003;15(1):23–32. 10.1016/s1044-5323(02)00125-2. - PubMed
-
- Tong X, Zeng H, Gu P, Wang K, Zhang H, Lin X. Monocyte chemoattractant protein–1 promotes the proliferation, migration and differentiation potential of fibroblast–like synoviocytes via the PI3K/P38 cellular signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(3):1623–32. 10.3892/mmr.2020.10969. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

