The impact of electronic health literacy on emotional management ability among college students: the mediating roles of peer relationships and exercise self-efficacy
- PMID: 39696508
- PMCID: PMC11658042
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-024-02276-6
The impact of electronic health literacy on emotional management ability among college students: the mediating roles of peer relationships and exercise self-efficacy
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to explore electronic health literacy's impact on college students' emotional management ability and analyze the chained mediating effects of peer relationships and exercise self-efficacy.
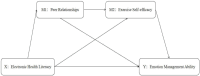
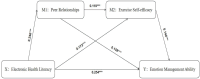
Methods: The study used stratified, cluster, and staged sampling methods to collect demographic information. Electronic health literacy, peer relationships, exercise self-efficacy, and emotional management ability data were collected among college students using the Questionnaire Star software. A total of 30,105 valid questionnaires were obtained, with a valid response rate of 98.7%. Using Process Model 6, investigated how electronic health literacy sequentially influences emotional management ability through mediators such as peer relationships and exercise self-efficacy.
Results: There was a significant positive correlation between electronic health literacy and emotional management ability (r = 0.496, P < 0.01), between electronic health literacy and peer relationships (r = 0.226, P < 0.01), and between electronic health literacy and exercise self-efficacy (r = 0.180, P < 0.01). Peer relationships were significantly positively correlated with exercise self-efficacy (r = 0.142, P < 0.01) and emotional management ability (r = 0.396, P < 0.01). Exercise self-efficacy was significantly positively correlated with emotional management ability (r = 0.339, P < 0.01). Electronic health literacy significantly and positively predicted emotional management ability (β = 0.254, P < 0.001). There was a mediating effect of peer relationships between electronic health literacy and emotional management ability, accounting for 58.2% of the impact, 95%CI: [0.036,0.042]. Exercise self-efficacy also mediated the relationship between electronic health literacy and emotional management ability, accounting for 61.5% of the effect, 95%CI: [0.022,0.027]. Moreover, a chained mediating effect of peer relationships and exercise self-efficacy was observed between electronic health literacy and emotional management ability, accounting for 17.1% of the effect, 95%CI: [0.004,0.005].
Conclusion: Electronic health literacy among college students can positively predict emotional management ability. Both peer relationships and exercise self-efficacy play a chained mediating role between electronic health literacy and emotional management ability.
Keywords: College Students; Electronic Health literacy; Emotional management ability; Exercise Self-efficacy; Mediating Effect; Peer relationships.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Nantong University (2022 [70]). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects included in the study. All methods of this study were performed following relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mayer JD, Salovey P. what is emotional intelligence; 1997.
-
- Guimond S, Ling G, Drodge J, Matheson H, Wojtalik JA, Lopez B, Collin G, Brady R, Mesholam-Gately RI, Thermenos H, et al. Functional connectivity associated with improvement in emotion management after cognitive enhancement therapy in early-course schizophrenia. Psychol Med. 2022;52(12):2245–54. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bohus M, Stoffers-Winterling J, Sharp C, Krause-Utz A, Schmahl C, Lieb K. Borderline personality disorder. Lancet. 2021;398(10310):1528–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- KYCX24_3498/Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
- BLA210215/General Program of Education of the National Social Science Fund of China: "Research on sports regulation mechanism and intervention scheme of middle school students' psychological pressure"
- B/2022/01/173/Key Project of Jiangsu Provincial Education Science Planning
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical