Drug susceptibility testing of Nocardia spp. using the disk diffusion method
- PMID: 39696557
- PMCID: PMC11657736
- DOI: 10.1186/s12941-024-00768-2
Drug susceptibility testing of Nocardia spp. using the disk diffusion method
Abstract
Background: Drug susceptibility testing (DST) for Nocardia spp. is essential to initiate effective antibiotic therapy. Currently, the only recommended technique is the determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) by microdilution. This method can be tedious to perform, despite the availability of ready-to-use plates. Herein, the aim was to determine the critical inhibition diameters specific to Nocardia spp.
Methods: MICs of 134 Nocardia isolates were determined by microdilution. Interpretative categories (Susceptible/Intermediate/Resistant) were determined using Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute breakpoints. In parallel, disk diffusion DST was performed. Receiver-operating-characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed to determine the inhibition diameter value that best discriminated between susceptible and non-susceptible strains (intermediate/resistant). The category agreement (CA), the rate of major (maj) and very major (vmj) discrepancies between microdilution and disk diffusion method was calculated.
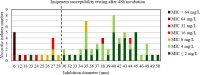
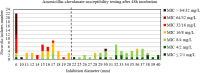
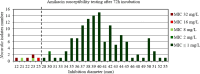
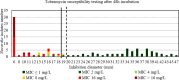
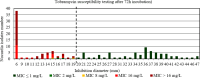
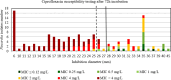
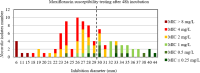
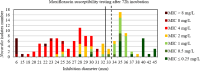
Results: For tobramycin, the critical diameter of 19 mm (diameter ≤ 19 mm = resistant strain; diameter > 19 mm = susceptible strain) provided a CA of 98.5%, 0.0% vmj, and 2.9% maj discrepancies, reaching strictly the acceptable performance criteria defined by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). For amikacin, the critical diameter of 25 mm (diameter ≤ 25 mm = resistant strain; diameter > 25 mm = susceptible strain) provided a CA of 98.5%, 0.0% vmj, and 1.5% maj discrepancies. For imipenem, excluding N. farcinica and N. cyriacigeorgica, the critical diameter of 29 mm (diameter ≤ 29 mm = resistant strain; diameter > 29 mm = susceptible strain), provided a CA of 98.6%, 0.0% vmj, and 0.0% maj discrepancies. Despite an estimated vmj rate 0.0%, the 95%-confident-interval exceeded the FDA criteria due to an insufficient number of amikacin/imipenem-resistant strains. For other tested antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, ceftriaxone, cotrimoxazole, linezolid), the FDA criteria were not reached.
Conclusions: Although the FDA criteria were mostly unmet, disk diffusion DST was suitable to accurately categorize Nocardia isolates into interpretative categories for the aminoglycosides and imipenem only, excluding species N. farcinica and N. cyriacigeorgica.
Keywords: Nocardia spp.; Critical inhibition diameters; Disk diffusion; Drug susceptibility testing; Microdilution.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Margalit I, Lebeaux D, Tishler O, Goldberg E, Bishara J, Yahav D et al. How do I manage nocardiosis? Clin Microbiol infect off publ eur soc clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021;27:550–8. - PubMed
-
- Ott SR, Meier N, Kolditz M, Bauer TT, Rohde G, Presterl E, et al. Pulmonary nocardiosis in Western Europe-Clinical evaluation of 43 patients and population-based estimates of hospitalization rates. Int J Infect Dis IJID off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis. 2019;81:140–8. - PubMed
-
- CASFM_2013.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 16]. https://www.sfm-microbiologie.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/CASFM_2013.pdf
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

