PD-1 interactome in osteosarcoma: identification of a novel PD-1/AXL interaction conserved between humans and dogs
- PMID: 39696578
- PMCID: PMC11658327
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01935-w
PD-1 interactome in osteosarcoma: identification of a novel PD-1/AXL interaction conserved between humans and dogs
Abstract
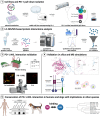
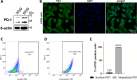
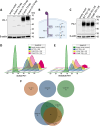
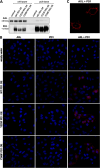
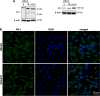
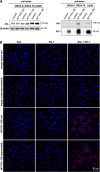
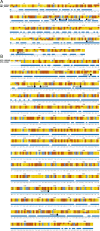
The PD-1/PDL-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors revolutionized cancer treatment, yet osteosarcoma remains a therapeutic challenge. In some types of cancer, PD-1 receptor is not solely expressed by immune cells but also by cancer cells, acting either as a tumor suppressor or promoter. While well-characterized in immune cells, little is known about the role and interactome of the PD-1 pathway in cancer. We investigated PD-1 expression in human osteosarcoma cells and studied PD-1 protein-protein interactions in cancer. Using U2OS cells as a model, we confirmed PD-1 expression by western blotting and characterized its intracellular as well as surface localization through flow cytometry and immunofluorescence. High-throughput analysis of PD-1 interacting proteins was performed using a pull-down assay and quantitative mass spectrometry proteomic analysis. For validation and molecular modeling, we selected tyrosine kinase receptor AXL-a recently reported cancer therapeutic target. We confirmed the PD-1/AXL interaction by immunoblotting and proximity ligation assay (PLA). Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations uncovered binding affinities and domain-specific interactions between extracellular (ECD) and intracellular (ICD) domains of PD-1 and AXL. ECD complexes exhibited strong binding affinity, further increasing for the ICD complexes, emphasizing the role of ICDs in the interaction. PD-1 phosphorylation mutant variants (Y223F and Y248F) did not disrupt the interaction but displayed varying strengths and binding affinities. Using bemcentinib, a selective AXL inhibitor, we observed reduced binding affinity in the PD-1/AXL interaction, although it was not abrogated. To facilitate the future translation of this finding into clinical application, we sought to validate the interaction in canine osteosarcoma. Osteosarcoma spontaneously occurs at significantly higher frequency in dogs and shares close genetic and pathological similarities with humans. We confirmed endogenous expression of PD-1 and AXL in canine osteosarcoma cells, with PD-1/AXL interaction preserved in the dog cells. Also, the interacting residues remain conserved in both species, indicating an important biological function of the interaction. Our study shed light on the molecular basis of the PD-1/AXL interaction with the implication for its conservation across species, providing a foundation for future research aimed at improving immunotherapy strategies and developing novel therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: AXL; Cancer-intrinsic PD-1; Comparative medicine; Immune checkpoints; Osteosarcoma; PD-1; Protein conservation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

