Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction modulates hypoxia and lipid toxicity to alleviate pulmonary vascular remodeling of pulmonary hypertension in rats
- PMID: 39696593
- PMCID: PMC11657759
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-01039-0
Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction modulates hypoxia and lipid toxicity to alleviate pulmonary vascular remodeling of pulmonary hypertension in rats
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a severe cardio-pulmonary vascular disease, involves complex molecular mechanism especially during the pathological process of pulmonary vascular remodeling, brings a significant challenge to clinical treatment and thus resulting in high mortality rates. Classic Traditional Chinese medicine formula, Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction (ZXGD), holds therapeutic potential for PH. In present study, we sought to explore therapeutic potential of ZXGD against PH in rats.
Methods: We employed a combination methods of chemical profiling, echocardiographic, morphologic measurements, molecular biology, rats models and cultured pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) to achieve this.
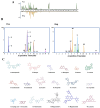
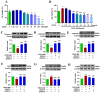
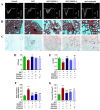
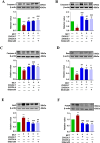
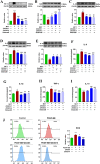
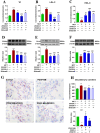
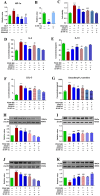
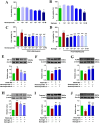
Results: Eighteen compounds were precisely identified in ZXGD using UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. Our data demonstrated ZXGD could alleviate PH by reducing pulmonary artery pressure and alleviating pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats. Specifically, ZXGD was found to intervene in abnormal expansion of PASMCs, thereby attenuating pulmonary vascular remodeling. ZXGD was also observed to modulate expressions of HIF-1α, ROS, and Nrf2 to alleviate hypoxia and oxidative stress. Additionally, ZXGD significantly regulated disorders in pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus mitigating inflammation. Furthermore, ZXGD decreased levels of decadienyl-L-carnitine and LDL-C, while elevating HDL-C and lipid droplet counts, thereby reducing cholesterol and lipid toxicity and preserving mitochondrial function. Importantly, inhibition of HIF-1α reversed expression of key pathological triggers for pulmonary vascular remodeling. Neohesperidin and naringin in ZXGD extract were identified as the primary contributors to its pharmacological effects against PH.
Conclusion: Altogether, our study empirically explored therapeutic potential and pharmacological mechanisms of ZXGD in treating PH, offering a groundwork for the development of novel anti-PH drugs.
Keywords: Chemical compounds; HIF-1α; Pulmonary hypertension; Pulmonary vascular remodeling; Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were approved by the Ethical Committee of Laboratory Animals at Harbin Medical University. Consent for publication: All authors agree to publish this article. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the Mechanism of Zhishi-Xiebai-Guizhi Decoction for the Treatment of Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Analyses.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(26):2059-2074. doi: 10.2174/0113816128293601240523063527. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38867532
-
[Effect of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction on phenotypic transformation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Oct;49(19):5297-5306. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240611.703. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39701768 Chinese.
-
Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction for coronary heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jan 19;103(3):e36588. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036588. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38241594 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Active Constituents and Molecular Mechanism of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction in the Treatment of CHD Based on UPLC-UESI-Q Exactive Focus, Gene Expression Profiling, Network Pharmacology, and Experimental Validation.ACS Omega. 2022 Jan 28;7(5):3925-3939. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04491. eCollection 2022 Feb 8. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35155889 Free PMC article.
-
[Coronary heart disease: innovative understanding from traditional Chinese medicine and treatment by classic formulas].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jul;49(13):3684-3692. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240326.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39041141 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Ruopp NF, Cockrill BA. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a review. JAMA. 2022;327(14):1379–91. - PubMed
-
- Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Souza R, Idrees M, Kawut SM, Sliwa-Hahnle K, et al. A global view of pulmonary hypertension. Lancet Respir Med. 2016;4(4):306–22. - PubMed
-
- Lau EMT, Giannoulatou E, Celermajer DS, Humbert M. Epidemiology and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017;14(10):603–14. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

