Enhancing employee job satisfaction through organizational climate and employee happiness at work: a mediated-moderated model
- PMID: 39696658
- PMCID: PMC11657427
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-024-02269-5
Enhancing employee job satisfaction through organizational climate and employee happiness at work: a mediated-moderated model
Abstract
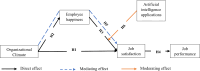
Background: The Chinese educational sector is dynamic; hence, there is a need to anchor the factors that influence faculty job satisfaction and performance. These are channeled through organizational climate (OrgC) and employee happiness (EmH). The growing integration of artificial intelligence applications (AIAs)-like ChatGPT-into the learning environment raises questions about AIAs' moderating role in the relationship between EmH at work and EJoS.
Purpose: This research empirically examines the influence of OrgC on EmH, the direct and mediated impacts of EmH on EJoS, and the moderating effect of AIAs on the influence of EmH on EJoS.
Design/methodology: Data was collected from faculty members of various Chinese universities. Using SmartPLS version 4.1, I have analyzed six hypotheses and the corresponding research questions.
Findings: The outcomes include favorable effects of OrgC on EmH and EJoS. EmH significantly correlates with EJoS, partially mediating the relationship between OrgC and EJoS. Interestingly, the research did not find evidence that AIAs moderated the relationship (ChatGPT) between EmH and EJoS. The predictors (OrgC and EmH) and moderation of AIAs explained a 51.9% change in EJoS, and EJoS explained a 13.3% variance in employee job performance.
Conclusion: This study's findings support a supportive OrgC as the key instrument for improving employees' happiness and job satisfaction. AI assistants, such as ChatGPT, provide relative efficiency and support but do not significantly affect how EmH at work relates to job satisfaction.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence applications; Employee happiness; Employee performance; Job satisfaction; Organizational climate.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The research followed the Ethical Principles of the American Psychological Association and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Weifang University of Science and Technology, China. It was made sure that the protection of rights and privacy was ensured, no harm or stress would occur, and participation was on a completely voluntary basis. Protection of data and confidentiality were maintained; no ethical standard or guideline was violated. Informed consent: Respondents were assured that participation in this research was strictly voluntary and that they could withdraw at any stage without any possible consequences. It was also assured that the responses would be kept confidential and used for research only. They consented to the completion and submission of the survey. Publication consent: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hmoud H, Al-Adwan AS, Horani O, Yaseen H, Zoubi JZA. Factors influencing business intelligence adoption by higher education institutions. J Open Innovation: Technol Market Complex. 2023;9(3):100111.
-
- Abdullahi MS, Raman K, Solarin SA, Adeiza A. Employee engagement as a mediating variable on the relationship between employee relation practice and employee performance in a developing economy. J Appl Res High Educ. 2023;15(1):83–97.
-
- Almuayad KMA, Chen Y. Effect of Knowledge Management on Employee Job Performance in Yemeni Banking Sector: the mediating role of job satisfaction. J Knowl Econ 2024.
-
- Indrayani I, Nurhatisyah N, Damsar D, Wibisono C. How does millennial employee job satisfaction affect performance? High Educ Skills Work-Based Learn. 2024;14(1):22–40.
-
- Layek D, Koodamara NK. Motivation, work experience, and teacher performance: a comparative study. Acta Psychol. 2024;245:104217. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources