Tim-3 pathway dysregulation and targeting in sepsis-induced immunosuppression
- PMID: 39696711
- PMCID: PMC11656820
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-024-02203-w
Tim-3 pathway dysregulation and targeting in sepsis-induced immunosuppression
Abstract
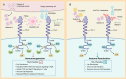
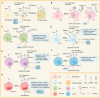
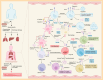
Sepsis is a major medical problem which causes millions of deaths worldwide every year. The host immune response in sepsis is characterized by acute inflammation and a simultaneous state of immunosuppression. In the later stage of sepsis, immunosuppression is a crucial factor that increases the susceptibility of septic patients to secondary infection and mortality. It is characterized by T cell exhaustion, excessive production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, hyperproliferation of immune suppressor cells and aberrant expression of immune checkpoint molecules. T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (Tim-3), an immune checkpoint molecule, is found on the surface of various cells, including macrophages, NK cells, NKT cells, and T cells. There are four different ligands for Tim-3, and accumulating evidence indicates that Tim-3 and its ligands play a crucial role in regulating immune cell dysfunction during sepsis. Anti-Tim-3 antibodies have been applied in the field of cancer immunotherapy and have achieved positive therapeutic effects in some clinical trials. However, the therapeutic efficacy of Tim-3 blockade is still controversial in animal models of sepsis. These challenges highlight the need for a deeper understanding of Tim-3 signaling in sepsis. This review examines the comprehensive effect of Tim-3 signaling in the development of sepsis-induced immunosuppression and the therapeutic efficacy of Tim-3 blockade.
Keywords: Immune checkpoint; Immunosuppression; Sepsis; Tim-3.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune checkpoint molecule Tim-3 promotes NKT cell apoptosis and predicts poorer prognosis in Sepsis.Clin Immunol. 2023 Sep;254:109249. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109249. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36736642
-
Tim-3 regulates sepsis-induced immunosuppression by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in CD4 T cells.Mol Ther. 2022 Mar 2;30(3):1227-1238. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.12.013. Epub 2021 Dec 18. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34933101 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of the T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain protein 3 pathway exacerbates sepsis-induced immune deviation and immunosuppression.Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Nov;178(2):279-91. doi: 10.1111/cei.12401. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24945079 Free PMC article.
-
The role of TIM-3 in sepsis: a promising target for immunotherapy?Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1328667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1328667. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38576606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research progress on T-cell immunoglobulin mucin 3/galectin 9 (TIM-3/galectin-9) in tumour immunity].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Aug;40(8):754-760. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39215674 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Targeting the immuno-inflammatory-microbial network: a key strategy for sepsis treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 14;16:1575516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1575516. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40297590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of transvesicoscopic Cohen and transvesicoscopic Politano-Leadbetter ureteral reimplantation in the treatment of ureterovesical junction obstruction (UVJO) in children: a single-center long-term follow-up study.Pediatr Surg Int. 2025 Mar 31;41(1):103. doi: 10.1007/s00383-025-06005-x. Pediatr Surg Int. 2025. PMID: 40164793 Free PMC article.
-
T cell-related diagnostic model and the underlying mechanism related to PRF1-mediated glycolysis in sepsis: evidences from single-cell, bulk transcriptomics, and experiment validation.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Aug 11;30(1):727. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02956-y. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40784892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):801–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer S, Fleischmann-Struzek C, Machado FR, Reinhart KK, Rowan K, Seymour CW, Watson RS, West TE, Marinho F, Hay SI, Lozano R, Lopez AD, Angus DC, Murray CJL, Naghavi M. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. The Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200–11. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van der Poll T, Shankar-Hari M, Wiersinga WJ. The immunology of sepsis. Immunity. 2021;54(11):2450–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

