A diagnostic index for predicting heart rate variability decline and prognostic value in newly diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer patients
- PMID: 39697224
- PMCID: PMC11652349
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1463805
A diagnostic index for predicting heart rate variability decline and prognostic value in newly diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer patients
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: A diagnostic index for predicting heart rate variability decline and prognostic value in newly diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer patients.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 12;15:1566535. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1566535. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40012554 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Heart rate variability (HRV) is an important marker of autonomic nervous system function and cardiovascular health. Holter monitoring is a crucial method for evaluating HRV, but the procedure and result analysis are relatively complex. This study aims to develop a simplified diagnostic index for predicting HRV decline in newly diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and evaluate its prognostic value.
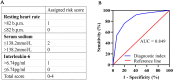
Methods: This retrospective cross-sectional study included 131 newly diagnosed NSCLC patients. Baseline characteristics were compared between normal HRV group and declined HRV group. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses identified significant predictors of HRV decline. A diagnostic index was developed based on resting heart rate (RHR), serum sodium, and interleukin-6 (IL-6) and externally validated. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis assessed the prognostic value of the index.
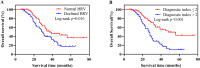
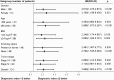
Results: Patients with declined HRV had higher median RHR (84 b.p.m. vs. 70 b.p.m., p < 0.001), lower serum sodium (136.3 mmol/L vs. 138.7 mmol/L, p < 0.001), lower serum albumin (39 g/L vs. 41 g/L, p = 0.031), higher lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (202 U/L vs. 182 U/L, p = 0.010), and higher IL-6 (11.42 pg/ml vs. 5.67 pg/ml, p < 0.001). Multivariate analysis identified RHR (OR = 3.143, p = 0.034), serum sodium (OR = 6.806, p < 0.001), and IL-6 (OR = 3.203, p = 0.033) as independent predictors of HRV decline. The diagnostic index, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.849, effectively predicted HRV decline. ROC analysis of the external validation data demonstrated an AUC of 0.788. Survival analysis showed that patients with a diagnostic index > 2 had significantly worse overall survival (log-rank p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The study identified key clinical parameters that predict HRV decline in newly diagnosed NSCLC patients. The developed diagnostic index, based on RHR, serum sodium, and IL-6, effectively stratifies patients by HRV status and has significant prognostic value, aiding in early identification and management of high-risk patients.
Keywords: diagnostic index; heart rate variability; interleukin-6; non-small cell lung cancer; overall survival; resting heart rate; serum sodium.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Liu, Han, Wang, Geng, Ding and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Predictive Value of Serum Calcium on Heart Rate Variability and Cardiac Function in Type 2 Diabetes Patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 14;13:864008. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.864008. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35498438 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum thioredoxin and DJ-1 in non-small cell lung carcinoma patients.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):1949-58. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3994-x. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26334622
-
Interplay of heart rate variability and resting heart rate on mortality in type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2024 Jan;18(1):102930. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2023.102930. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38150792
-
Development of a Novel Predictive-Prognostic Scoring Index for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Cureus. 2023 Jan 1;15(1):e33234. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33234. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36733552 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic models for newly-diagnosed chronic lymphocytic leukaemia in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 31;7(7):CD012022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012022.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32735048 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

