The role of FDG PET assessment in patients with advanced breast cancer treated with cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in the second-line setting
- PMID: 39697231
- PMCID: PMC11653356
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1454844
The role of FDG PET assessment in patients with advanced breast cancer treated with cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in the second-line setting
Abstract
Background: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors have demonstrated a survival benefit in the second-line treatment of patients with hormone receptor-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer. However, identifying prognostic biomarkers remains a challenge. Thus, we aimed to assess the prognostic value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography (FDG-PET-CT) performed before CDK4/6 inhibitors initiation.
Methods: This single-center retrospective analysis comprised patients treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors in the second-line setting between 2018 and 2024, with FDG-PET-CT performed before CDK4/6 inhibitor initiation.
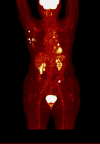
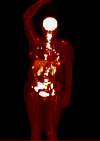
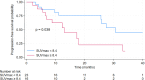
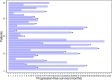
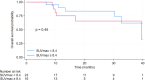
Results: The study included 39 patients with a median age of 63 years (IQR 50 -71). Among them, 12 had de novo metastatic disease (30.8%), and 13 had oligometastatic disease (33.3%). Treatment distribution was as follows: 15 patients received palbociclib (38%), 19 ribociclib (49%), and five abemaciclib (13%). Most patients received fulvestrant (31 patients, 79%), whereas eight patients (21%) were treated with letrozole. The median progression-free survival (PFS) in all studied patients was 25.8 months. Notably, baseline SUVmax (maximum standardized uptake value) showed statistically and clinically significant differences. Patients in the low SUVmax group had a median PFS of 30.7 months, compared to 13.0 months for those in the high SUVmax group (p = 0.038). The 2-year PFS was 76.2% [95% CI 51.8% - 89.4%] for the low SUVmax group, contrasting with 22.3% [95% CI 4.0% - 49.9%] for the high SUVmax group. High SUVmax, poor performance status, and de novo metastatic disease were independent prognostic factors for PFS.
Conclusions: FDG-PET-CT performed before cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor commencement is a valuable prognostic tool in hormone receptor-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer. Patients with SUVmax less than 8.4 experienced extended progression-free survival compared to those with higher SUVmax.
Keywords: 18Ffluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography; abemaciclib; advanced breast cancer; palbociclib; ribociclib.
Copyright © 2024 Kubeczko, Polakiewicz-Gilowska, D’Amico, Chrabański, Świderska, Chmielik, Blamek, Handkiewicz-Junak and Jarząb.
Conflict of interest statement
MK declares advisory board for Novartis; speaker's honoraria from Novartis, Roche, MSD, Pfizer, Lilly, Teva, Amgen, Swixx Biopharma, and Gilead; clinical trials for Roche, MSD, Novartis, Seagen, and Gilead; conference fees for Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, Teva, Amgen, Gilead, MSD, and Swixx Biopharma; all outside the submitted work. AP-G declares conferences fees for Pfizer, clinical trials for Roche, MSD, Novartis, Seagen, Gilead; speaker's honorarium: Pfizer, Novartis, Gilead; all outside the submitted work. KS declares conferences fees: Novartis, clinical studies: Roche, MSD, Novartis; speaker's honorarium: Novartis; all outside the submitted work. MJ declares conference fees for Gilead, Roche; clinical trials for Roche, MSD, Novartis, Seagen, and Gilead; speaker's honoraria from Novartis, Roche, Lilly, Pfizer, Teva, Exact Sciences, Mammotome, and Gilead; advisory boards for Novartis and Pfizer; all outside submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Fasching PA, De Laurentiis M, Im SA, et al. . Phase III randomized study of ribociclib and fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: MONALEESA-3. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:2465–72. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.78.9909 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

