Serum IL-23 levels reflect a myeloid inflammatory signature and predict the response to apremilast in patients with psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 39697337
- PMCID: PMC11652657
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1455134
Serum IL-23 levels reflect a myeloid inflammatory signature and predict the response to apremilast in patients with psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
Background: The phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor apremilast downregulates the production of IL-23 and other pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Aim: To investigate the effects of apremilast on the production of cytokines by peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages, innate-like lymphocyte cells (ILCs), mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, γδ T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and NKT-like cells from patients with PsA manifesting different clinical responses to the treatment.
Methods: Peripheral blood samples were obtained from patients with PsA at baseline and after 1 and 4 months of apremilast therapy (n = 23) and 20 controls with osteoarthritis. Cytokine expression in peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages and ILCs/MAIT/γδT/NK/NKT-like cells was tested by RT-PCR and FACS analyses, respectively; cytokine levels in culture supernatants and sera were analyzed by ELISA.
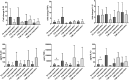
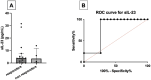
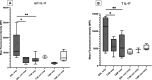
Results: PsA monocyte-derived macrophages exhibited higher expressions of IL-23, IL-1β, and TNF-α, compared with OA controls, more profoundly in patients responding to apremilast. There were 17/23 (74%) PsA patients who were classified as responders to apremilast at 4 months, and a baseline serum IL-23 >1.4 pg/mL was associated with the responder status (AUCROC 0.79; sensitivity 100%, specificity 68%). Of note, apremilast led to a significantly reduced expression of IL-23 in peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages; IL-17 in ILC1 and in T cells of responder patients; IFN-γ in γδ T lymphocytes.
Conclusion: An enhanced myeloid inflammatory signature characterizes PsA monocyte-derived macrophages, and serum IL-23 levels represent candidate biomarkers for PsA response to apremilast.
Keywords: cytokines; immunology; innate lymphocyte; macrophages; precision medicine; spondyloarthritis (including psoriatic arthritis).
Copyright © 2024 De Santis, Tonutti, Isailovic, Motta, Rivara, Ragusa, Guidelli, Caprioli, Ceribelli, Renna, Luciano and Selmi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors received funding and consultation fees from Amgen.
Figures


References
-
- Coates LC, Soriano ER, Corp N, Bertheussen H, Callis Duffin K, Campanholo CB, et al. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA): updated treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis 2021. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18:465–79. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00798-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nerviani A, Boutet MA, Tan WSG, Goldmann K, Purkayastha N, Lajtos TA, et al. IL-23 skin and joint profiling in psoriatic arthritis: novel perspectives in understanding clinical responses to IL-23 inhibitors. Ann Rheumatic Diseases. (2021) 80:591–7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218186 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ, Gomez-Reino JJ, Adebajo AO, Wollenhaupt J, Gladman DD, et al. Treatment of psoriatic arthritis in a phase 3 randomised, placebo-controlled trial with apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. Ann Rheum Dis. (2014) 73:1020–6. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205056 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

