Real-world comparison of palbociclib, abemaciclib, and dalpiciclib as first-line treatments for Chinese HR+/HER2-metastatic breast cancer patients: a multicenter study (YOUNGBC-28)
- PMID: 39697620
- PMCID: PMC11653472
- DOI: 10.1177/17588359241302018
Real-world comparison of palbociclib, abemaciclib, and dalpiciclib as first-line treatments for Chinese HR+/HER2-metastatic breast cancer patients: a multicenter study (YOUNGBC-28)
Abstract
Background: In recent years, the combination of CDK4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) and endocrine therapy (ET) has emerged as the standard first-line treatment for hormone receptor positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative (HER2-) metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients. However, the comparison between the efficacy of CDK4/6i has been poorly explored before. Moreover, it remains unclear about the optimal choice of CDK4/6i in the first-line treatment for HR+/HER2- MBC patients in Asian, especially Chinese populations.
Objectives: Our study aims to compare the efficacy of three CDK4/6i widely used in the Chinese population (palbociclib, abemaciclib, and dalpiciclib) in the real world.
Design: From 2020 to 2023, the medical records of patients diagnosed with HR+/HER2- MBC were retrospectively assessed in seven institutions in China. Patients who received first-line palbociclib, abemaciclib, or dalpiciclib plus ET were included.
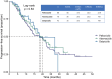
Methods: Demographic and clinical data were retrospectively collected and analyzed. Real-world progression-free survival (rwPFS), overall survival (OS), and objective response rate were used to analyze the clinical outcome.
Results: In total, 209 HR+/HER2- MBC patients were eligible for this study. Eighty-eight (42.1%), 79 (37.8%), and 42 (20.1%) patients were administered first-line palbociclib, abemaciclib, or dalpiciclib plus ET. The overall median rwPFS was 19 months, with no significant difference between these three CDK4/6i (p = 0.84). The results were similar even after propensity score matching. The median OS was not reached. Cox univariate and multivariate regression analysis identified that higher KI67 index, liver metastasis, and primary endocrine resistance were independent risk factors for rwPFS in patients with initial CDK4/6i plus ET.
Conclusion: This study presents a comparison of the real-world efficacy between three CDK4/6i widely used in the Chinese population. Palbociclib, abemaciclib, and dalpiciclib demonstrated comparable efficacy in Chinese patients with advanced HR+/HER2- MBC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT06344780.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitors; abemaciclib; dalpiciclib; endocrine therapy; metastatic breast cancer; palbociclib; real world.
© The Author(s), 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, et al.. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023; 73: 17–48. - PubMed
-
- Finn RS, Martin M, Rugo HS, et al.. Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2016; 375: 1925–1936. - PubMed
-
- Cristofanilli M, Turner NC, Bondarenko I, et al.. Fulvestrant plus palbociclib versus fulvestrant plus placebo for treatment of hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer that progressed on previous endocrine therapy (PALOMA-3): final analysis of the multicentre, double-blind, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2016; 17: 425–439. - PubMed
-
- Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, et al.. Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2016; 375: 1738–1748. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, et al.. Phase III randomized study of ribociclib and fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: MONALEESA-3. J Clin Oncol 2018; 36: 2465–2472. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

