Flow cytometry for extracellular vesicle characterization in COVID-19 and post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 39697632
- PMCID: PMC11648478
- DOI: 10.20517/evcna.2024.20
Flow cytometry for extracellular vesicle characterization in COVID-19 and post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
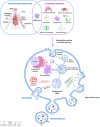
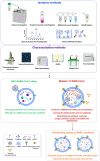
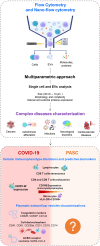
Infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19 diseases, can impact different tissues and induce significant cellular alterations. The production of extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are physiologically involved in cell communication, is also altered during COVID-19, along with the dysfunction of cytoplasmic organelles. Since circulating EVs reflect the state of their cells of origin, they represent valuable tools for monitoring pathological conditions. Despite challenges in detecting EVs due to their size and specific cellular compartment origin using different methodologies, flow cytometry has proven to be an effective method for assessing the role of EVs in COVID-19. This review summarizes the involvement of plasmatic EVs in COVID-19 patients and individuals with Long COVID (LC) affected by post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), highlighting their dual role in exerting both pro- and antiviral effects. We also emphasize how flow cytometry, with its multiparametric approach, can be employed to characterize circulating EVs, particularly in infectious diseases such as COVID-19, and suggest their potential role in chronic impairments during post-infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; Long COVID; Multidistrict infection; PASC; SARS-CoV-2; biomarkers; flow cytometry; multiparametric analysis.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Fanelli M and Petrone V reported that financial support was provided by HERVCOV project funded by the HORIZONHLTH-2021-DISEASE G.A.101057302. The other authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. General principles of cell communication. In: Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Science; 2002. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26813/ . [Last accessed on 8 Aug 2024]
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
