Endosomal escape mechanisms of extracellular vesicle-based drug carriers: lessons for lipid nanoparticle design
- PMID: 39697635
- PMCID: PMC11648457
- DOI: 10.20517/evcna.2024.19
Endosomal escape mechanisms of extracellular vesicle-based drug carriers: lessons for lipid nanoparticle design
Abstract
The rise of biologics and RNA-based therapies challenges the limitations of traditional drug treatments. However, these potent new classes of therapeutics require effective delivery systems to reach their full potential. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as a promising solution for RNA delivery, but endosomal entrapment remains a critical barrier. In contrast, natural extracellular vesicles (EVs) possess innate mechanisms to overcome endosomal degradation, demonstrating superior endosomal escape (EE) compared to conventional LNPs. This mini review explores the challenges of EE for lipid nanoparticle-based drug delivery, and offers insights into EV escape mechanisms to advance LNP design for RNA therapeutics. We compare the natural EE strategies of EVs with those used in LNPs and highlight contemporary LNP design approaches. By understanding the mechanisms of EE, we will be able to develop more effective drug delivery vehicles, enhancing the delivery and efficacy of RNA-based therapies.
Keywords: RNA therapeutics; drug delivery; endosomal escape; extracellular vesicles; lipid nanoparticles; membrane fusion.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Merkel OM is a consultant for Corden Pharma GmbH, AMW GmbH, and PARI Pharma GmbH. Furthermore, Merkel OM is an advisory board member for Coriolis Pharma GmbH and a consultant for AbbVie Deutschland GmbH on unrelated projects. The other authors have declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
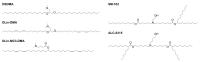


References
-
- Kesharwani P, Banerjee S, Gupta U, et al. PAMAM dendrimers as promising nanocarriers for RNAi therapeutics. Mater Today. 2015;18:565–72. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2015.06.003. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
