Retrospective Study of CD20 Expression Loss in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- PMID: 39697682
- PMCID: PMC11650554
- DOI: 10.14740/jh1341
Retrospective Study of CD20 Expression Loss in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abstract
Background: CD20-targeted therapies are widely used in the management of B-cell lymphomas. Re-treatment with CD20-directed agents is common; however, previous research has demonstrated loss of CD20 expression at relapse in a subset of patients.
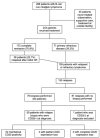
Methods: In this single-center retrospective cohort of 243 patients, CD20 analysis was performed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and/or flow cytometry at diagnosis and at relapse if a biopsy was performed.
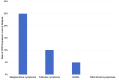
Results: Of 109 patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphoma, 59 patients with CD20-positive lymphoma at diagnosis underwent a biopsy at relapse for a total of 76 biopsies across all relapses. The rate of partial or complete CD20 expression loss was 11.9% (four patients with partial loss, three patients with complete loss). There were four cases of CD20 loss at first relapse (three IHC, one flow cytometry), two at second relapse (one IHC, one IHC and flow cytometry), and one at fifth relapse (IHC and flow cytometry). CD20 antigen escape was observed in marginal zone lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). All patients with CD20 expression loss previously received rituximab. Among patients with CD20 antigen escape, 85.7% had stage IV disease, and median overall survival after CD20 loss was 4 months. In the group of five patients with indolent lymphoma and CD20 expression loss, three patients (60%) had concurrent transformation to high-grade lymphoma.
Conclusions: This study, which reinforces the importance of repeating a biopsy at relapse before implementing CD20-directed therapy, is particularly relevant given the widespread use of rituximab along with the emerging significance of CD20-targeted bispecific antibodies in the management of B-cell lymphomas.
Keywords: Antigen escape; CD20; Lymphoma; Rituximab.
Copyright 2024, Marshalek et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Cd20 Expression and Effects on Outcome of Relapsed/ Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma after Treatment with Rituximab.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Feb 26;19(2):331-335. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.2.331. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 29479962 Free PMC article.
-
Histological and immunophenotypic changes in 59 cases of B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma after rituximab therapy.Cancer Sci. 2009 Jan;100(1):54-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.01005.x. Epub 2008 Nov 25. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19038008 Free PMC article.
-
Odronextamab, a human CD20×CD3 bispecific antibody in patients with CD20-positive B-cell malignancies (ELM-1): results from the relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma cohort in a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1 trial.Lancet Haematol. 2022 May;9(5):e327-e339. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(22)00072-2. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Lancet Haematol. 2022. PMID: 35366963 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Loss of CD20 antigen expression after rituximab therapy of CD20 positive B cell lymphoma (diffuse large B cell extranodal marginal zone lymphoma combination): a case report and review of the literature.Med Oncol. 2012 Jun;29(2):1223-6. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-9955-3. Epub 2011 Jul 31. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21805377 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
