Comparison of postoperative radiotherapy and definitive radiotherapy for non-metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck, a propensity score matching based on the SEER database
- PMID: 39697727
- PMCID: PMC11651770
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-24-1221
Comparison of postoperative radiotherapy and definitive radiotherapy for non-metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck, a propensity score matching based on the SEER database
Abstract
Background: Treating patients with head and neck adenoid cystic carcinoma (HNACC) presents surgical problems in various scenarios. Limited studies explore definitive radiation's impact on patient survival, with inadequate data correlating it to postoperative radiotherapy. Using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program, we conducted an objective analysis to evaluate the impact of definitive radiation on the survival of HNACC patients without distant metastases, aiming to uncover its nuanced pros and cons.
Methods: This study conducted a comprehensive analysis of individuals diagnosed with HNACC within the SEER database from 2000 to 2023. Disease-specific survival (DSS) and overall survival (OS) were evaluated using diverse statistical methods. Propensity score matching (PSM) reduced covariate variations and selection biases, allowing for comparisons of postoperative and definitive radiotherapy groups.
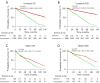
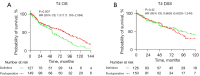
Results: A total of 2,072 patients were encompassed within this study. The postoperative radiotherapy group yielded significant advantages in OS and DSS (P<0.001). In matched cohorts, the 5-year prognostic OS stood at 55% and 37%, respectively, while DSS figures were 65% and 46%, correspondingly. In advanced T4 cases, DSS differences lacked significance (P=0.42). Additionally, the outcomes of OS and DSS were notably influenced by variables such as T-stage, N-stage, tumor stage, and chemotherapy.
Conclusions: Surgical intervention remains a pivotal component of comprehensive treatment for patients diagnosed with operable HNACC. Definitive radiation is appropriate for less treatable situations, particularly in local advanced HNACC. Systemic treatment may assist HNACC patients at risk of distant metastases.
Keywords: Head and neck cancer; Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (SEER database); adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC); definitive radiotherapy; postoperative radiotherapy.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-24-1221/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of postoperative radiotherapy for non-metastatic head and neck adenoid cystic carcinoma based on SEER data.J Int Med Res. 2022 Aug;50(8):3000605221115151. doi: 10.1177/03000605221115151. J Int Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35929027 Free PMC article.
-
Role of postoperative radiotherapy in resected adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck.Radiat Oncol. 2022 Dec 1;17(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02165-5. Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36456955 Free PMC article.
-
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Larynx: A SEER Database Review.Ear Nose Throat J. 2022 Nov;101(9):587-592. doi: 10.1177/0145561320970691. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022. PMID: 33170034
-
Head & neck acinar cell carcinoma: a population-based study using the seer registry.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jul 8;20(1):631. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07066-y. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32641007 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical significance for primary tumor surgery in metastatic head and neck adenoid cystic carcinoma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Oct;280(10):4577-4586. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08043-4. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37261520
Cited by
-
Long-term survival of subglottic adenoid cystic carcinoma: a case report.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 28;15:1611107. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1611107. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40792278 Free PMC article.
-
A case report of adenoid cystic carcinoma combined with giant renal metastasis treated with robotic surgery.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 18;16(1):1368. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03197-5. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40679668 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
