Bioinformatics analysis reveals VEGFC's prognostic significance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its association with immune cell infiltration
- PMID: 39697755
- PMCID: PMC11651743
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-24-834
Bioinformatics analysis reveals VEGFC's prognostic significance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its association with immune cell infiltration
Abstract
Background: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) has a poor prognosis due to late diagnosis and complex molecular mechanisms. Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) is associated with angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. This study aimed to investigate VEGFC's prognostic value in HNSCC and its correlation with immune cell infiltration.
Methods: VEGFC gene expression was analyzed in HNSCC patients using Tumor Immune Estimation Resource 2.0 (TIMER2.0), Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA), and University of ALabama at Birmingham CANcer data analysis Portal (UALCAN) databases, focusing on differential expression and clinical-pathological correlations. The impact of VEGFC on overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) was assessed using GEPIA. RNA-seq profiles and clinical information from 503 HNSCC tumor tissues and 44 normal control tissues obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database were subjected to univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses to develop a prognostic nomogram. The Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING) database was used for a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, while the Tumor-Immune System Interaction Database (TISIDB) for immune-related associations. Expression was further validated with the Gene Expression Omnibus dataset (GSE6631) and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR).
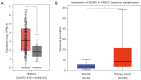
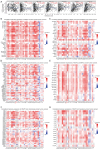
Results: VEGFC was significantly upregulated in HNSCC and closely correlated with age, gender, race, and tumor stage (P<0.05). PPI and co-expression gene analysis identified ITGA3, NT5E, and PXN as highly associated with VEGFC (R>0.6, P<0.05), which are mainly enriched in PI3K/Akt, MAPK signaling pathway, and cancer-associated glycoproteins. High VEGFC expression predicted poor OS (P=0.003) and DFS (P=0.03). Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses confirmed VEGFC as an independent prognostic factor for HNSCC. The prognostic nomogram accurately predicted 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival and calibration curve was very close to ideal 45-degree diagonal line. VEGFC also correlated with immune cells infiltration, including B cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, as well as immune-related markers such as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) markers, immune modulators, and inflammatory chemokines (P<0.05).
Conclusions: VEGFC may serve as an independent prognostic factor and potential immunotherapeutic target in HNSCC, offering insights into patient risk stratification and personalized treatment strategies.
Keywords: Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC); bioinformatics; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC); immune infiltration; prognosis.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-24-834/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
