Oral self-management of palbociclib using mobile technology: Findings from a nurse-led randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 39697813
- PMCID: PMC11653135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apjon.2024.100604
Oral self-management of palbociclib using mobile technology: Findings from a nurse-led randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: Test the feasibility and effectiveness of a text message reminder intervention for the self-management of oral anticancer medication in patients with metastatic breast cancer.
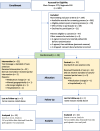
Methods: Forty-three females initiating treatment with palbociclib participated in a two-armed prospective randomized clinical trial. Participants were randomized into the control (n = 21) and intervention groups (n = 22) from January 2020 to January 2023. Survey responses were collected at three-time points; (1) at consent, (2) end of treatment cycles, and (3) at a follow-up clinic visit. Surveys included a demographic questionnaire, the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire, post-study assessment, and the R-15 Participant Satisfaction Questionnaire. Nurse providers completed the Adaptation of Stamps Nurse Workload questionnaire.
Results: The COVID-19 pandemic and regulatory decisions supporting other CDK4/6 medications negatively influence recruitment; thus, a small sample for each arm only detected large differences between the two arms regarding effectiveness. Feasibility analysis was not conducted due to insufficient data, but the participants frequently used their smartphones for text messaging. Although the survey data were limited, participants provided anecdotal information supporting the use of text messaging as a positive method to remind them to take their medication, have their labs drawn, and attend MD visits. Participants would have liked text messages at the exact time they took their medications as a simple reminder.
Conclusions: Given the importance of cancer treatments and the difficulties patients experience during these treatments, text messages using smartphones can actively improve patients' engagement and their ability to manage their treatment regimens.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov; ID: NCT04216576.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Clinical oncology; Clinical trial; Text telecommunications.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Dr. Barton-Burke served as the Recipients of a 10.13039/100004319Pfizer Grant supporting this research. Dr. Barton-Burke serves on the editorial board of the Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing. The article underwent standard review procedures of the journal, with peer review conducted independently of Dr. Barton-Burke and their research groups.
Figures
References
-
- Finn R.S., Crown J.P., Lang I., et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment for estrogen receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): a randomized phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015 Jan 1;16(1):25–35. - PubMed
-
- Wilkes G.M., Barton-Burke M. Jones and Bartlett Learning; 2019 Dec 2. 2020-2021) Oncology Nursing Drug Handbook.
-
- Thakkar J., Kurup R., Laba T.L., et al. Mobile telephone text messaging for medication adherence in chronic disease: a meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2016 Mar 1;176(3):340–349. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical