Preparation of atorvastatin calcium-loaded liposomes using thin-film hydration and coaxial micromixing methods: A comparative study
- PMID: 39697814
- PMCID: PMC11653151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100309
Preparation of atorvastatin calcium-loaded liposomes using thin-film hydration and coaxial micromixing methods: A comparative study
Abstract
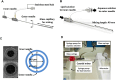
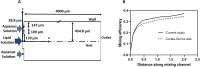
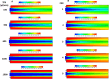
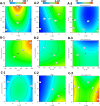
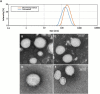
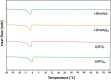
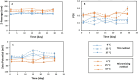
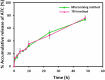
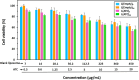
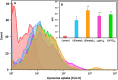
Development of techniques to produce nanoformulations in a controlled and reproducible manner is of great importance for research, clinical trials, and industrial scale-up. This research aimed to introduce a cost-effective micromixing approach for the nanoassembly of liposomes and compared with thin-film hydration (TFH) method. Numerical simulations and design of experiments (DOE) by response surface methodology (RSM) were used to evaluate the effects of input parameters on liposome properties, aiming to identify optimal conditions. Anionic liposomes without or with atorvastatin calcium (ATC) produced using TFH and the micromixing methods showed similar characteristics in size (150-190 nm), PDI (<0.2), and zeta potential (-50 to -60 mV). Both methods achieved about 70 % encapsulation efficiency with similar drug release profile for ATC-containing liposomes. Analysis of stability and DSC thermograms revealed comparable outcomes for liposomes prepared using both techniques. Nanoliposomes produced via both approaches indicated similar in vitro biological performance regarding cellular uptake and cell viability. The micromixing approach presented an alternative method to produce nanoliposomes in a one-step manner with high controllability and reproducibility without requiring specialized equipment. Compatibility of the micromixer with various solvents, including those detrimental to conventional microfluidic materials like PDMS and thermoplastics, enables exploration of a wide range of formulations.
Keywords: Coaxial micromixer; Comparison; Controllability; Microfluidics; Nanoliposome; Reproducibility; Thin-film hydration.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aghaei H., Nazar A.R.S., Varshosaz J. Double flow focusing microfluidic-assisted based preparation of methotrexate–loaded liposomal nanoparticles: encapsulation efficacy, drug release and stability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021;614
-
- Akar S., Taheri A., Bazaz R., Warkiani E., Shaegh M. Twisted architecture for enhancement of passive micromixing in a wide range of Reynolds numbers. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2021;160
-
- Akar S., Fardindoost S., Hoorfar M. High throughput microfluidics-based synthesis of PEGylated liposomes for precise size control and efficient drug encapsulation. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces. 2024;238 - PubMed
-
- Akl M.A., Ryad S., Ibrahim M.F., Kassem A.A. Formulation, and optimization of transdermal atorvastatin calcium-loaded ultra-flexible vesicles; ameliorates poloxamer 407-caused dyslipidemia. Int. J. Pharm. 2023;638 - PubMed
-
- Akl M.A., Ryad S., Ibrahime M.F., Kassem A.A. Ultraflexible liposomes for transdermal delivery of atorvastatin calcium: rheological and ex vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2024;126:2400048.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

