Composition and antimicrobial activity of hydroalcoholic extracts of Pleurotus eryngii var. ferulae and P. eryngii var. elaeoselini
- PMID: 39697823
- PMCID: PMC11652160
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1498787
Composition and antimicrobial activity of hydroalcoholic extracts of Pleurotus eryngii var. ferulae and P. eryngii var. elaeoselini
Abstract
Background: The basidiomycetes Pleurotus eryngii var. ferulae Lanzi and P. eryngii var. elaeoselini Venturella et al. belong to the P. eryngii species complex, acting as facultative biotrophs in association with members of Apiaceae family, i.e., Ferula communis L. and Elaeoselinum asclepium L., respectively. The consumption of these fungi has rapidly increased in recent decades, not only thanks to their nutritional properties and pleasant flavor, but also for their bioactive and medicinal properties.
Methods: A quantitative study of their hydroalcoholic extracts was carried out by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. The potential antimicrobial activity of the extracts was also tested against some phytopathogenic bacteria [Clavibacter michiganensis and Bacillus megaterium (Gram-positive), Pseudomonas viridiflava, Xanthomonas campestris, and Escherichia coli (Gram-negative)] and fungi (Aspergillus fumigatus, Penicillium italicum, Monilinia laxa, Botrytis cinerea, Cadophora sp., and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum).
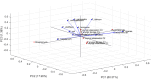
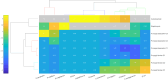
Results: The chemical analysis allowed the identification of secondary metabolites belonging to different classes, as flavonoids, organic acids, amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, nucleic acids, fatty acids, and triterpenoids. Both extracts demonstrated antimicrobial activity against of the most tested microorganisms.
Conclusion: The results can broaden the knowledge on the possible use of these fungal species in the agricultural sector.
Keywords: LC-MS; Pleurotus eryngii var. elaeoselini; Pleurotus eryngii var. ferulae; antibacterial activity; antifungal activity.
Copyright © 2024 Polito, De Martino, Mirabile, Venturella, Gargano, De Feo, Elshafie and Camele.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Akyuz M., Kirbag S. (2009). Antimicrobial activity of Pleurotus eryngii var. ferulae grown on various agro-wastes. EurAsian J. Biosci. 3, 58–63. 10.5053/ejobios.2009.3.0.8 - DOI
-
- Akyüz M., Onganer A. N., Erecevit P., Kirbag S. (2012). Flavonoid contents and 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging activity of some edible mushrooms from Turkey: A. bisporus and Pleurotus spp. Cur. Top. Nutraceut. R. 10, 133.
-
- Amamcharla J. K., Metzger L. E. (2014). Modification of the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay to determine the susceptibility of raw milk to oxidation. Int. Dairy J. 34, 177–179. 10.1016/j.idairyj.2013.09.004 - DOI
-
- Angeles Flores G., Girometta C. E., Cusumano G., Angelini P., Tirillini B., Ianni F., et al. (2022). Untargeted metabolomics used to describe the chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of extracts from Pleurotus spp. mycelium grown in different culture media. Antibiotics 11, 1468. 10.3390/antibiotics11111468 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

