Guidelines for the standardized diagnosis and treatment of non-specific orbital inflammation (2024)
- PMID: 39697897
- PMCID: PMC11589454
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2024.12.07
Guidelines for the standardized diagnosis and treatment of non-specific orbital inflammation (2024)
Abstract
Non-specific orbital inflammation (NSOI) is a non-infectious orbital inflammation. Although it is often considered the most common diagnosis in orbital biopsies, it is an exclusionary diagnosis that requires ruling out systemic disease or other possible causes. Its characteristics include acute orbital signs and symptoms, including pain, proptosis, periorbital edema, chemosis, diplopia, and visual impairment. The clinical manifestations and histological findings of NSOI are heterogeneous, without specific diagnostic criteria or treatment guidelines, which poses significant challenges for diagnosis and treatment. This guideline provides a detailed description of the definition, classification, diagnosis, and treatment of NSOI.
Keywords: clinical manifestation; diagnosis; non-specific orbital inflammation; treatment.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Shao Y, None; Ma JM, None; Yang HS, None; Expert Workgroup of Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonspecific Orbital Inflammation (2024), None; Ophthalmic Imaging and Intelligent Medicine Branch Chinese Medicine Education Association, None; Ocular Oncology Committee of the Ophthalmology Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association, None; Ophthalmology Committee of International Association of Translational Medicine, None; Ophthalmology Committee of International Association of Intelligent Medicine, None; Chinese Ophthalmic Imaging Study Groups, None.
Figures
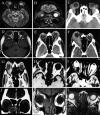
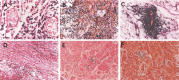
Similar articles
-
Non-specific orbital inflammation: Current understanding and unmet needs.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 Mar;81:100885. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100885. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32717379 Review.
-
Nonspecific Orbital Inflammation.2024 May 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 May 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31869057 Free Books & Documents.
-
Man with a Swollen Eye: Nonspecific Orbital Inflammation in an Adult in the Emergency Department.J Emerg Med. 2018 Jul;55(1):110-113. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 30. J Emerg Med. 2018. PMID: 29716820
-
Central serous chorioretinopathy associated with nonspecific orbital inflammation: a case report.J Int Med Res. 2024 Mar;52(3):3000605241233963. doi: 10.1177/03000605241233963. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38436326 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic orbital myositis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1997 Nov;9(6):504-12. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199711000-00005. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1997. PMID: 9375279 Review.
References
-
- Birch-Hirschfeld A. Diagnosis of the benign and malignant tumors of the orbit. Der Deutsch Ophthalmol Ges. 1905;32:127–135.
-
- Grove AS, Jr, Weber AL. Orbital pseudotumor—historical origin and modern relevance. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;29(5):341–346. - PubMed
-
- Shields JA, Shields CL. Orbital pseudotumor versus idiopathic nongranulomatous orbital inflammation. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;29(5):349. - PubMed
-
- Günalp I, Gündüz K, Yazar Z. Idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1996;74(2):191–193. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
