Ketogenic Diet Reduces Age-Induced Chronic Neuroinflammation in Mice
- PMID: 39697898
- PMCID: PMC11654834
- DOI: 10.59368/agingbio.20240038
Ketogenic Diet Reduces Age-Induced Chronic Neuroinflammation in Mice
Abstract
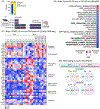
The ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) is an acidic energy metabolite that is synthesized during periods of fasting or exercise. Our previous study demonstrated that an every other week cyclic ketogenic diet (Cyclic KD), which induces blood BHB levels similar to those observed during fasting, reduces midlife mortality and improves memory in aging mice. In addition to its canonical role as an energy metabolite, BHB regulates gene expression and inflammatory activation through non-energetic signaling pathways. The precise mechanisms by which BHB or KD affects brain function during aging remain incompletely understood. Using bulk RNA-sequencing (RNA-Seq), we examined whole brain gene expression of 12-month-old C57BL/6JN male mice fed KD for either one week or 14 months. While one-week KD increases some inflammatory gene expression, the 14-month Cyclic KD largely reduces age-induced neuroinflammatory gene expression. Next, a gene expression analysis of human primary brain cells (microglia, astrocytes, and neurons) using RNA-Seq revealed that BHB alone induces a mild level of inflammation in all three cell types. However, BHB inhibits the more pronounced inflammatory gene expression induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in microglia. BHB exhibits a comparable inhibitory effect on LPS-induced inflammation in mouse primary microglia, which we used as an in vitro model to test and exclude known mechanisms by which BHB regulates inflammation and gene expression as responsible for this modulation of LPS-induced inflammatory gene expression. An acidic milieu resulting from BHB may be required for or contribute to the effect. Overall, we observe that BHB has the potential to attenuate the microglial response to inflammatory stimuli, such as LPS. This may contribute to an observed reduction in chronic inflammation in the brain following long-term Cyclic KD treatment in aging mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest J.C.N. and E.V. are cofounders, stockholders, and coinventors on patents licensed to BHB Therapeutics, Ltd., and Selah Therapeutics Ltd., which develop ketone esters for consumer and therapeutic use.
Figures



Update of
-
A ketogenic diet reduces age-induced chronic neuroinflammation in mice Running title: ketogenic diet and brain inflammaging.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 4:2023.12.01.569598. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.01.569598. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Aging Biol. 2024;2:20240038. doi: 10.59368/agingbio.20240038. PMID: 38106160 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
