A Cross-Sectional Study Assessing Saudi Population's Awareness Toward the Relationship Between Oral Health and Overall Well-Being
- PMID: 39697929
- PMCID: PMC11653044
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.73880
A Cross-Sectional Study Assessing Saudi Population's Awareness Toward the Relationship Between Oral Health and Overall Well-Being
Abstract
Background and aim: Oral health constitutes a critical component of overall health. Additionally, there is evidence of a bidirectional interaction between oral health and the progression of chronic diseases. Many chronic illnesses present oral manifestations and thus can impact oral health but conversely, oral health, particularly the presence of oral bacteria, can influence the progression of chronic diseases. Consequently, a comprehensive understanding of this relationship is essential, as it has significant implications for both oral and overall health. This study aimed to evaluate the knowledge of the Saudi population about oral health and its association with systemic diseases, as well as the factors that might affect this knowledge including demographics and educational level.
Methods: A structured questionnaire using multiple-choice questions was developed in Arabic language and distributed among patients visiting the Dental Teaching Hospital of Umm AlQura University. An electronic version of the questionnaire was developed using Google Forms for distribution through social media outlets. The data were analyzed using SPSS, version 29 (Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.). Descriptive statistics, chi-square test, and Fisher's exact test were used to analyze the data, and the significance level was set at p<0.05. Participants were considered to have good oral health knowledge and awareness if they answered 60% of the questions correctly.
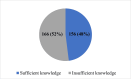
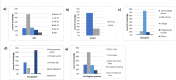
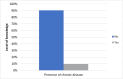
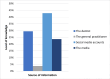
Result: Most participants were female (66.5%), predominantly aged 20-29 years. More than half of the participants (166; 52%) reported insufficient knowledge regarding oral health. Additionally, there was a significant association between gender and the level of knowledge (p<0.001), with females exhibiting a higher level of knowledge compared to males. Furthermore, there was a significant association between the source of information and the level of knowledge (p=0.009) with participants who reported social media as their primary source of information being more likely to have sufficient knowledge.
Conclusion: Since more than half of the surveyed individuals demonstrated a deficiency in oral health knowledge, there is a necessity for enhanced awareness and educational initiatives regarding the implications of oral health on general health within the Saudi population.
Keywords: awarness; knowledge; oral health; overall well-being; public health.
Copyright © 2024, Bamaga et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. The Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of Umm Al-Qura University issued approval #HAPO-02-K-012-2023-02-1465. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
