Prevalence of Traumatic Dental Injuries and Associated Risk Factors Among Preschool Children in Goa: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39697948
- PMCID: PMC11653226
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.73894
Prevalence of Traumatic Dental Injuries and Associated Risk Factors Among Preschool Children in Goa: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background and aim: Primary teeth trauma has received very little attention compared to permanent teeth due to their eventual exfoliation. Enamel discolorations, hypoplasias, and enamel-surface abnormalities have been reported in the permanent dentition following primary tooth trauma. Traumatic dental injuries (TDI) also have an impact on the quality of life of an individual. The study aims to determine the prevalence of TDI and its association with various risk factors in preschool children in the state of Goa. The primary objective is to determine the prevalence of TDI in primary anterior teeth in preschool children in the state of Goa. The secondary objective is to determine the association of various risk factors with TDI in preschool children in the state of Goa.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted among preschool children aged three to five years across the state of Goa. A total of 971 children were included in the study. Parents or guardians of participants who reported trauma answered an interview addressing the history of the injury. The anterior dental trauma and associated factors such as age, gender, time of injury, month of injury, place of injury, occlusal relationship, lip competence, oral habits, and ordinal position of the child were assessed and analyzed.
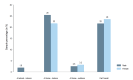
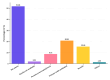
Results: Out of the 971 children examined, TDI was reported in 157 (16.1%) children. Of these, 83 of 157 (52.8%) children had experienced TDI at home. Three-year-old children had the highest TDI prevalence of any age group, with 32 of 145 (22.0%) experiencing TDI. The most commonly affected tooth (100 of 233, 10.3%) was the primary maxillary right central incisor. Of the 233 traumatized teeth, 100 (42.9%) had code 2 injuries (enamel fractures only), which were the most frequently reported injuries. Mesio-incisal angle fracture was detected in 84 (34.3%) teeth affected with TDI. With respect to the number of teeth traumatized, 99 of 157 (63.0%) of children had a single tooth traumatized. Among all children who had sustained TDI, 103 (65.6%) were firstborns, 50 (31.8%) were secondborns, and four (2.5%) were thirdborn children. Only eight children received treatment, of which seven received medications and only one child received dental treatment. Parents being unaware of TDI was the main reason for not seeking treatment.
Conclusions: This study highlights the critical need for educating parents and teachers about TDI prevention and the importance of prompt dental care. The findings offer valuable insights for formulating state- and national-level policies and preventive strategies for managing TDI.
Keywords: cross-sectional studies; humans; pediatric dentistry; preschool children; prevalence; risk factors; tooth injuries epidemiology; traumatology.
Copyright © 2024, Borkar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Goa Dental College and Hospital Institutional Ethics Committee issued approval GDCH/IEC/VII-2022 (08)-PROV. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- World traumatic dental injury prevalence and incidence, a meta-analysis-one billion living people have had traumatic dental injuries. Petti S, Glendor U, Andersson L. Dent Traumatol. 2018;34:71–86. - PubMed
-
- Prevalence of traumatic dental injuries and associated factors among preschool children in Amman, Jordan. ElKarmi RF, Hamdan MA, Rajab LD, Abu-Ghazaleh SB, Sonbol HN. Dent Traumatol. 2015;31:487–492. - PubMed
-
- Exploring the profile of articles on traumatic dental injuries in pediatric dental journals. Feldens CA, Kramer PF, Feldens EG. Dent Traumatol. 2013;29:172–177. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources