Exosome-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of diabetes and its complications: current opinion
- PMID: 39698026
- PMCID: PMC11648477
- DOI: 10.20517/evcna.2023.32
Exosome-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of diabetes and its complications: current opinion
Abstract
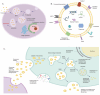
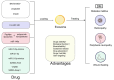
Diabetes medication is based on controlling blood glucose and delaying the onset of related complications and is not a complete cure for diabetes. Conventional drug therapy fails to stop progressive islet β cell failure in diabetic patients. Recent studies have shown that "exosome-based therapy" holds great promise in treating diabetes and its complications. Exosomes are small vesicles that are stable in the bloodstream and can effectively deliver therapeutic drugs to specific tissues or organs through intercellular communication. Using exosomes as carriers for drug delivery offers several advantages. This review summarizes the benefits of exosomal drug delivery systems, drug loading methods, and their applications in treating diabetes and its complications. However, there are still challenges to overcome in using exosomal drug delivery systems, such as large-scale production, assessing the contents of exosomes, and monitoring the safety and effectiveness of the treatment in vivo. In conclusion, this review proposes the therapeutical potential of exosomes as drug carriers for developing novel drugs to provide new strategies for treating diabetes and its complications.
Keywords: Exosomes; diabetes; diabetic complications; drug carrier.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
