Oscillometry reference values for children and adolescents
- PMID: 39698065
- PMCID: PMC11655022
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00278-2024
Oscillometry reference values for children and adolescents
Abstract
Background: Oscillometry devices allow quantification of respiratory function at tidal breathing but device-specific reference equations are scarce: the present study aims to create sex-specific oscillometric reference values for children and adolescents using the Resmon PRO FULL device.
Methods: Healthy participants (n=981) aged 6 to 17 years of the Austrian LEAD general population cohort were included. Subjects had normal weight (body mass index ≤99th percentile) and normal lung volumes (total lung capacity (TLC) ≥ lower limit of normal). Oscillometry data were collected using a single frequency mode of 8 Hz. Sex-specific prediction equations were developed for total, inspiratory and expiratory resistance (R) and reactance (X) as well as for the modulus of impedance (Z) value using the LMS (lambda, mu, sigma) method. Height was used as a single covariate.
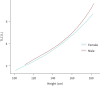
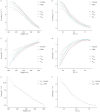
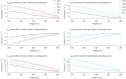
Results: Reference equations for all oscillometry parameters were created for Caucasian children aged 6 to 17 years with a height span from 101 to 183 cm and a lung volume span from 1.7 to 8.8 L TLC. R and Z values progressively decrease and X values increase with increasing height. Oscillometry parameters versus lung volume curves differ from those versus height curves. Stratified for lung size, no sex differences are found for oscillometry parameters.
Conclusion: Our study provides reference values for oscillometry parameters in children and adolescents using strictly defined criteria for weight and lung volumes. No sex-related differences in oscillometry parameters corrected for height or lung size are found.
Copyright ©The authors 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: P.P. Pompilio and A. Gobbi are co-founders and serve as board members of RESTECH s.r.l., a company that designs, manufactures and sells devices for lung function testing based on the forced oscillation technique. The other authors have nothing to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
