Four distinct cytoplasmic structures generate and release specific vesicles, thus opening the way to intercellular communication
- PMID: 39698300
- PMCID: PMC11648438
- DOI: 10.20517/evcna.2023.03
Four distinct cytoplasmic structures generate and release specific vesicles, thus opening the way to intercellular communication
Abstract
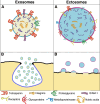
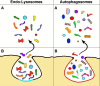
In all cells, generation and release of specific vesicles are the initial steps of back-and-forth intercellular communication. These processes are critical in normal physiology and pathophysiology. Vesicles have particular functions appropriate to their targets. When stimulated, they are released into the extracellular space. Four cytoplasmic membrane-bound structures generate their particular vesicles. Among these structures, multivesicular bodies (MVBs) can accumulate many small vesicles in their lumen; release occurs upon MVB exocytosis. Ectosomes are larger vesicles characterized by their responses and are generated directly and released independently from specific microdomains pre-established in the thickness of the plasma membrane. Most lysosomes do not generate vesicles. However, unique components of a minor form, the endo-lysosome, constitute the third class of structures that release a few vesicles by exocytosis with molecules and structures inducing changes in the extracellular environment. The autophagosome, the fourth structure, releases several heterogeneous vesicles by exocytosis with malformed bio-molecules, assembled structures, and damaged organelles. Interestingly, the frequent interaction of autophagosomes with MVBs and their exosomes contributes to the regulation and intensity of their action. The specificity and function of released vesicles depend on their membranes' and luminal cargoes' composition and dynamics. An ongoing investigation of the various vesicles reveals new properties regarding their generation, release, and resulting extracellular processes. The growth of information about structures and their vesicles progressively extends the knowledge base regarding cell communication and contributes to their clinical applications.
Keywords: Autophagosomes; cargo; ectosomes and exosomes; endo-lysosomes; endocytosis; exocytosis; extracellular vesicles (EVs); lysosome storage disorders (LSDs); membrane fusions; microdomains; multivesicular bodies (MVBs); unconventional protein secretion (UPS).
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, Orr L, Turbide C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with Johnston RM released vesicles (exosomes) J Biol Chem. 1987;262:9412–20. - PubMed
-
- Heijenen HF, Schlel AE, Fijnheer R, Geuze HJ, Sixma JJ. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and a-granules. Blood. 1999;94:3791–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
