Comparative study of trastuzumab modification analysis using mono/multi-epitope affinity technology with LC-QTOF-MS
- PMID: 39698314
- PMCID: PMC11652880
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101015
Comparative study of trastuzumab modification analysis using mono/multi-epitope affinity technology with LC-QTOF-MS
Abstract
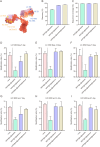
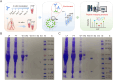
Dynamic tracking analysis of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) biotransformation in vivo is crucial, as certain modifications could inactivate the protein and reduce drug efficacy. However, a particular challenge (i.e. immune recognition deficiencies) in biotransformation studies may arise when modifications occur at the paratope recognized by the antigen. To address this limitation, a multi-epitope affinity technology utilizing the metal organic framework (MOF)@Au@peptide@aptamer composite material was proposed and developed by simultaneously immobilizing complementarity determining region (CDR) mimotope peptide (HH24) and non-CDR mimotope aptamer (CH1S-6T) onto the surface of MOF@Au nanocomposite. Comparative studies demonstrated that MOF@Au@peptide@aptamer exhibited significantly enhanced enrichment capabilities for trastuzumab variants in comparison to mono-epitope affinity technology. Moreover, the higher deamidation ratio for LC-Asn-30 and isomerization ratio for HC-Asn-55 can only be monitored by the novel bioanalytical platform based on MOF@Au@peptide@aptamer and liquid chromatography-quadrupole time of flight-mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF-MS). Therefore, multi-epitope affinity technology could effectively overcome the biases of traditional affinity materials for key sites modification analysis of mAb. Particularly, the novel bioanalytical platform can be successfully used for the tracking analysis of trastuzumab modifications in different biological fluids. Compared to the spiked phosphate buffer (PB) model, faster modification trends were monitored in the spiked serum and patients' sera due to the catalytic effect of plasma proteins and relevant proteases. Differences in peptide modification levels of trastuzumab in patients' sera were also monitored. In summary, the novel bioanalytical platform based on the multi-epitope affinity technology holds great potentials for in vivo biotransformation analysis of mAb, contributing to improved understanding and paving the way for future research and clinical applications.
Keywords: Biotransformation analysis; Breast cancer; LC-QTOF-MS; Monoclonal antibody; Multi-epitope affinity technology.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Xi’an Jiaotong University.
Conflict of interest statement
As an editorial board member, Zhengjin Jiang recused himself from all review processes related to this article to ensure the fairness and objectivity of the review. Other authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
In vitro/in vivo degradation analysis of trastuzumab by combining specific capture on HER2 mimotope peptide modified material and LC-QTOF-MS.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Sep 8;1225:340199. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.340199. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 36038230
-
Multiepitope recognition technology promotes the in-depth analysis of antibody‒drug conjugates.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Nov;14(11):4962-4976. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.06.007. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39664422 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS-Based Monitoring of In Vivo Protein Biotransformation: Quantitative Determination of Trastuzumab and Its Deamidation Products in Human Plasma.Anal Chem. 2016 Feb 2;88(3):1871-7. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04276. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Anal Chem. 2016. PMID: 26713683
-
Identification and Affinity Determination of Protein-Antibody and Protein-Aptamer Epitopes by Biosensor-Mass Spectrometry Combination.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 27;22(23):12832. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312832. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of B-cell lymphoid malignancies.BioDrugs. 2011 Feb 1;25(1):13-25. doi: 10.2165/11539590-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2011. PMID: 21090841 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro Stability Study of a Panel of Commercial Antibodies at Physiological pH and Temperature as a Guide to Screen Biologic Candidate Molecules for the Potential Risk of In vivo Asparagine Deamidation and Activity Loss.Pharm Res. 2025 Feb;42(2):353-363. doi: 10.1007/s11095-025-03825-3. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Pharm Res. 2025. PMID: 39979532 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

