The mediating role of psychological resilience in the relationship between physical exercise and sense of security among left-behind junior high school students: multi-group comparative analysis of only children and children with siblings
- PMID: 39698385
- PMCID: PMC11654250
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1411175
The mediating role of psychological resilience in the relationship between physical exercise and sense of security among left-behind junior high school students: multi-group comparative analysis of only children and children with siblings
Abstract
Background: This study aims to explore the mediating role of psychological resilience in the relationship between physical exercise and the sense of security among junior high school students, with a particular focus on variations based on only-child status.
Methods: A survey was conducted among 649 left-behind junior high school students in Gansu Province, China, utilizing the Physical Activity Rating Scale-3 (PARS-3), Security Questionnaire (SQ), and Resilience Scale for Chinese Adolescents (RSCA).
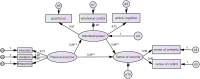
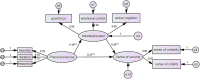
Results: Among the participants, the mean scores for physical exercise, psychological resilience, and sense of security were 40.78 ± 29.49, 51.14 ± 10.08, and 55.75 ± 14.35, respectively. A significant positive correlation was observed between physical exercise and sense of security (r = 0.210, p < 0.01), physical exercise and psychological resilience (r = 0.164, p < 0.01), and psychological resilience and sense of security (r = 0.443, p < 0.01). Mediation analysis revealed that psychological resilience partially mediates the effect of physical exercise on the sense of security, accounting for 33.9% of the total effect. Multi-group analysis indicated significant differences in this mediating effect between only children and children with siblings, with a stronger predictive role of psychological resilience for the sense of security among non-only children.
Conclusion: Participation in physical exercise can promote the improvement of sense of security through the individual power factor of improving the psychological resilience of left-behind junior high school students, and this improvement effect is more significant for non-only children.
Keywords: children with siblings; left-behind junior high school students; only children; physical exercise; psychological resilience; sense of security.
Copyright © 2024 Xia, Liu and Qin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdulaziz Muhsen T., Abdulaziz Muhsen M. (2020). The impact of physical activity and sport onmental health. J. Phys. Educ. 32, 160–165. doi: 10.37359/jope.v32 - DOI
-
- Al-Qahtani A. M., Shaikh M. A. K., Shaikh I. A. (2018). Exercise as a treatment modality for depression: a narrative review. Alexand. J. Med. 54, 429–435. doi: 10.1016/j.ajme.2018.05.004 - DOI
-
- Belcher B. R., Zink J., Azad A., Campbell C. E., Chakravartti S. P., Herting M. M. (2021). The roles of physical activity, exercise, and fitness in promoting resilience during adolescence: effects on mental well-being and brain development. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimag. 6, 225–237. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2020.08.005, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernardon S., Babb K. A., Hakim-Larson J., Gragg M. (2011). Loneliness, attachment, and the perception and use of social support in University students. Can. J. Behav. Sci. 43, 40–51. doi: 10.1037/a0021199 - DOI
-
- Blake J. (1981). The only child in America: prejudice versus performance. Popul. Dev. Rev. 7:43. doi: 10.2307/1972763 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

