Radiomics for predicting grades, isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation, and oxygen 6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation of adult diffuse gliomas: combination of structural MRI, apparent diffusion coefficient, and susceptibility-weighted imaging
- PMID: 39698654
- PMCID: PMC11652054
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-24-1110
Radiomics for predicting grades, isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation, and oxygen 6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation of adult diffuse gliomas: combination of structural MRI, apparent diffusion coefficient, and susceptibility-weighted imaging
Abstract
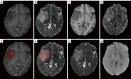
Background: There has been no research investigating susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) radiomics features in evaluating molecular makers in gliomas. The aim of this study was to assess the predictive value of radiomics features extracted from structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), and SWI in determining World Health Organization (WHO) Grade, isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation, and oxygen 6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation in patients with diffuse gliomas.
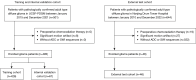
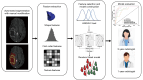
Methods: Retrospective MRI data of 539 patients from University of California San Francisco and Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital between January 2010 and December 2022 were analyzed in this study. The training, internal validation, and external test cohorts included 426 (median age 60 years, 168 female), 67 (median age 56 years, 31 female), and 46 (median age 55 years, 22 female) patients, respectively. A total of 7,896 radiomics features were extracted from structural MRI, ADC, and SWI within two regions of interest (ROIs). Feature selection was conducted using analysis of variance (ANOVA) F-test, and random forest was employed to establish predictive models. Chi-square test and Mann-Whitney U test were used for assessing the statistical differences in patients' clinical characteristics. Delong test was performed to compare the areas under the curve (AUCs) of different radiomics models.
Results: For WHO Grade task, the combined model of structural MRI, ADC, and SWI achieved the highest AUC of 0.951 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.886-1.000] on the external test cohort. For IDH mutation task, the structural MRI model achieved the highest AUC of 0.917 (95% CI: 0.801-1.000) on the external test cohort. For MGMT task, the combined model of structural MRI and ADC achieved the highest AUC of 0.650 (95% CI: 0.485-0.814) on the internal validation cohort.
Conclusions: The combined structural MRI, ADC, and SWI models achieved promising performance in assessing WHO Grade and IDH mutation status but showed no efficacy in predicting MGMT methylation status. Adding SWI and ADC features cannot provide extra information to structural MRI in predicting WHO grade and IDH mutation.
Keywords: Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI); apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC); isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH); machine learning; radiomics.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-24-1110/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Kleihues P, Ellison DW. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:803-20. 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, Brat DJ, Cree IA, Figarella-Branger D, Hawkins C, Ng HK, Pfister SM, Reifenberger G, Soffietti R, von Deimling A, Ellison DW. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Neuro Oncol 2021;23:1231-51. 10.1093/neuonc/noab106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
