Role of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging in preoperative tumor-node-metastasis staging evaluation of esophageal cancer: a narrative review
- PMID: 39698700
- PMCID: PMC11652015
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-24-34
Role of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging in preoperative tumor-node-metastasis staging evaluation of esophageal cancer: a narrative review
Abstract
Background and objective: Esophageal cancer (EC) is an aggressive disease characterized by high mortality rates and a propensity for locoregional or distant recurrence. The treatment strategies and prognostic estimation for EC depend on accurate pre-treatment tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging. The objective of this review was to illustrate the role of various imaging modalities in achieving accurate preoperative TNM staging of EC, with a particular focus on the utilization of advanced high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences for T classification, which have shown promise in enhancing the delineation of tumor depth and extent.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed and Web of Science databases. The studies on imaging in preoperative TNM staging of EC published in English from inception of these databases to December 31, 2022 were reviewed.
Key content and findings: The review highlights the distinct advantages and inherent limitations of different imaging modalities for the preoperative staging of EC. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) provides real-time, high-resolution imaging of the esophageal wall but is operator-dependent. Computed tomography (CT) is widely available and non-invasive, but it may lack sensitivity for early T-stage identification. Positron emission tomography (PET)/CT offers accurate assessment of distant metastasis but has limited value in the evaluation of early-stage tumors. With improved techniques, MRI is particularly useful for visualization of tumor infiltration and the surrounding anatomical structures, gaining prominence in preoperative staging of EC.
Conclusions: Various imaging modalities including EUS, CT, PET/CT, and MRI should be applied as complementary methods for preoperative TNM staging of EC. Notably, high-resolution MRI can overcome motion-related artifacts and provide high-quality images, which may play a more important role in the management of EC in the future.
Keywords: Esophageal cancer (EC); magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); preoperative assessment; tumor-node-metastasis staging (TNM staging).
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-24-34/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



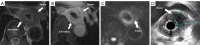

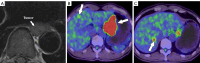
References
-
- Obermannová R, Alsina M, Cervantes A, Leong T, Lordick F, Nilsson M, van Grieken NCT, Vogel A, Smyth EC, ESMO Guidelines Committee . Electronic address: clinicalguidelines@esmo. Oesophageal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2022;33:992-1004. 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.07.003 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
