Farm-to-fork changes in poultry microbiomes and resistomes in Maputo City, Mozambique
- PMID: 39699181
- PMCID: PMC11748491
- DOI: 10.1128/msystems.01037-24
Farm-to-fork changes in poultry microbiomes and resistomes in Maputo City, Mozambique
Abstract
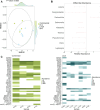
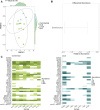
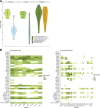
Increasing demand for poultry has spurred poultry production in low- and middle-income countries like Mozambique. Poultry may be an important source of foodborne, antimicrobial-resistant bacteria to consumers in settings with limited water, sanitation, and hygiene infrastructure. The Chicken Exposures and Enteric Pathogens in Children Exposed through Environmental Pathways (ChEEP ChEEP) study was conducted in Maputo City, Mozambique from 2019 to 2021 to quantify enteric pathogen exposures along the supply chain for commercial and local (i.e., scavenger) chicken breeds. Here, we performed metagenomic sequencing of total DNA from banked ChEEP ChEEP samples to characterize fecal and carcass microbiomes and resistome diversity between chicken breeds and along the supply chain. Fecal samples (n = 26) were collected from commercial and local chickens at production sites and markets and carcass (n = 49) and rinse bucket samples (n = 26) from markets. We conducted taxonomic profiling and identified antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) from metagenomic sequence data, focusing especially on potential human pathogens and "high-risk" ARGs. We estimated alpha diversity for each sample and compared by site and breed. We estimated Bray-Curtis dissimilarity between samples and examined clustering. We found that commercial and local chickens harbored distinct fecal potential pathogens and resistomes at production and market sites. Many potentially pathogenic bacteria and ARGs present in chicken fecal samples are also present on carcasses sold to consumers. Finally, commercial chicken carcasses contain high-risk ARGs that are not necessarily introduced from chicken feces. These results indicate markets are an important site of exposure to potentially pathogenic bacteria and high-risk ARGs.
Importance: While chicken eggs and meat are a critical protein source in low-income settings, antibiotics are routinely fed to chickens with consequences for selection of antimicrobial resistance. Evaluating how poultry gut bacterial communities, including potential human pathogens and high-risk antimicrobial resistance genes, differ from farm to market could help identify where to target interventions to minimize transmission risks to human populations. In this study in Maputo City, Mozambique, we found compositional differences between commercial and local chicken breeds at production and market sites. We also found that while all potentially pathogenic bacteria and many high-risk antimicrobial resistance genes persisted from production and market through processing, some resistance genes were detected on carcass samples only after processing, suggesting human or environmental contamination is occurring within markets. Overall, our findings indicate that open-air markets may represent a critical juncture for human exposures to pathogens and antimicrobial resistance genes from poultry and poultry products.
Keywords: East Africa; antibiotic resistance; markets; metagenomics; poultry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accumulation of microbial hazards and assessment of food hygiene associated with broiler chicken processing at open air food markets in Maputo, Mozambique.Int J Food Microbiol. 2025 Jan 16;427:110960. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2024.110960. Epub 2024 Nov 3. Int J Food Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39532025
-
More diversified antibiotic resistance genes in chickens and workers of the live poultry markets.Environ Int. 2021 Aug;153:106534. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106534. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Environ Int. 2021. PMID: 33799229
-
Quantifying Enteropathogen Contamination along Chicken Value Chains in Maputo, Mozambique: A Multidisciplinary and Mixed-Methods Approach to Identifying High Exposure Settings.Environ Health Perspect. 2023 Nov;131(11):117007. doi: 10.1289/EHP11761. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Environ Health Perspect. 2023. PMID: 37962439 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics in Canadian poultry productions and anticipated alternatives.Front Microbiol. 2014 Jun 17;5:282. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00282. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24987390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mercury Level in Worldwide Poultry Food Products: a Systematic Review.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 May 13. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04659-1. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40358913 Review.
References
-
- Erdaw MM, Beyene WTs. 2022. Trends, prospects and the socio-economic contribution of poultry production in sub-Saharan Africa: a review. Worlds Poult Sci J 78:835–852. doi:10.1080/00439339.2022.2092437 - DOI
-
- Grace D, Makita K, Bonfoh B. 2010. Safe food, fair food: participatory risk analysis for improving the safety of informally produced and marketed food in sub Saharan Africa.
-
- Raimundo I, Wagner J, Crush J, Abrahamo E, Mccordic C. 2020. Inclusive growth and informal vending in maputo’s food markets.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 5T32ES012870/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)
- T32AI138952/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- T32 ES007032/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32ES007032-37, 5T32ES012870-15/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)
- T32 AI138952/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

