SARS-CoV-2 resistance analyses from the Phase 3 PINETREE study of remdesivir treatment in nonhospitalized participants
- PMID: 39699245
- PMCID: PMC11823660
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01238-24
SARS-CoV-2 resistance analyses from the Phase 3 PINETREE study of remdesivir treatment in nonhospitalized participants
Abstract
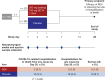
Remdesivir inhibits the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp; Nsp12). Here, we conducted viral resistance analyses from the Phase 3 PINETREE trial of remdesivir in nonhospitalized participants at risk of severe COVID-19. Nasopharyngeal swabs (collected at baseline [Day 1], Days 2, 3, 7, and 14) were eligible for analysis if their viral load was above the lower limit of quantification for the RT-qPCR assay (2228 copies/mL). The SARS-CoV-2 genome was sequenced for all remdesivir participants and 50% of placebo participants (baseline, Days 3, 7, and 14) and for participants who progressed to COVID-19-related hospitalization or all-cause death (all time points). Emergent substitutions in Nsp12 and other replication complex proteins were phenotyped using site-directed mutagenesis in a SARS-CoV-2 subgenomic replicon system. Overall, emergent Nsp12 substitutions were detected in 8/115 (7.0%) remdesivir participants and 7/129 (5.4%) placebo participants (1 substitution overlap between groups). Based on a structural analysis, none of the emergent Nsp12 substitutions were in direct contact with the incoming nucleoside triphosphate substrate, the RNA, or the RNA template 5' overhang. One substitution (A376V) showed reduced susceptibility to remdesivir (12.6-fold change in remdesivir half-maximal concentration [EC50]); it also showed reduced fitness when introduced in the SARS-CoV-2 replicon and virus in vitro. Other substitutions had <1.1-fold change in remdesivir EC50. None of the emergent substitutions in Nsp8, Nsp10, Nsp13, or Nsp14 (remdesivir, 10/115 [8.7%]; placebo, 10/129 [7.8%]) showed reduced remdesivir susceptibility. In conclusion, emergent substitutions in the SARS-CoV-2 RdRp complex with reduced remdesivir susceptibility were uncommon, indicating a high barrier to remdesivir resistance.CLINICAL TRIALSThis study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov as NCT04501952.
Keywords: drug therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
L.R., J.L., R.M., D.H., S.X., J.M., N.P., J.K.P., R.H.H., D.P.P., M.A., and C.H. are stockholders and employees of Gilead Sciences, Inc. H.W.L. has nothing to disclose. G.C. is a shareholder and former employee of Gilead Sciences, Inc., and an employee of Vir Biotechnology, Inc. M.G. received funding from Gilead Sciences, Inc., for studies on the mechanism of action of RDV.
Figures


References
-
- Lo MK, Jordan R, Arvey A, Sudhamsu J, Shrivastava-Ranjan P, Hotard AL, Flint M, McMullan LK, Siegel D, Clarke MO, Mackman RL, Hui HC, Perron M, Ray AS, Cihlar T, Nichol ST, Spiropoulou CF. 2017. GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit filo-, pneumo-, and paramyxoviruses. Sci Rep 7:43395. doi: 10.1038/srep43395 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sheahan TP, Sims AC, Graham RL, Menachery VD, Gralinski LE, Case JB, Leist SR, Pyrc K, Feng JY, Trantcheva I, Bannister R, Park Y, Babusis D, Clarke MO, Mackman RL, Spahn JE, Palmiotti CA, Siegel D, Ray AS, Cihlar T, Jordan R, Denison MR, Baric RS. 2017. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci Transl Med 9:eaal3653. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown AJ, Won JJ, Graham RL, Dinnon KH III, Sims AC, Feng JY, Cihlar T, Denison MR, Baric RS, Sheahan TP. 2019. Broad spectrum antiviral remdesivir inhibits human endemic and zoonotic deltacoronaviruses with a highly divergent RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Antiviral Res 169:104541. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.104541 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

