Thyroid hormone and the Liver
- PMID: 39699315
- PMCID: PMC11661762
- DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000596
Thyroid hormone and the Liver
Abstract
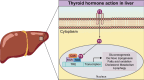
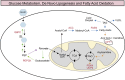
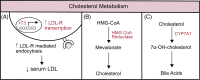
It is known that thyroid hormone can regulate hepatic metabolic pathways including cholesterol, de novo lipogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, lipophagy, and carbohydrate metabolism. Thyroid hormone action is mediated by the thyroid hormone receptor (THR) isoforms and their coregulators, and THRβ is the main isoform expressed in the liver. Dysregulation of thyroid hormone levels, as seen in hypothyroidism, has been associated with dyslipidemia and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Given the beneficial effects of thyroid hormone in liver metabolism and the advances illuminating the use of thyroid hormone analogs such as resmetirom as therapeutic agents in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, this review aims to further explore the relationship between TH, the liver, and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Herein, we summarize the current clinical therapies and highlight future areas of research.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrahepatic hypothyroidism in MASLD: Role of liver-specific thyromimetics including resmetirom.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2024 May;18(5):103034. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2024.103034. Epub 2024 May 4. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38714040 Review.
-
Thyromimetics and MASLD: Unveiling the Novel Molecules Beyond Resmetirom.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Feb;40(2):367-378. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16874. Epub 2025 Jan 16. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39817461 Review.
-
Hepatic thyroid hormone receptor-β signalling: Mechanisms and recent advancements in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Apr;27(4):1635-1647. doi: 10.1111/dom.16117. Epub 2024 Dec 10. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39658733 Review.
-
Direct effects of thyroid hormones on hepatic lipid metabolism.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018 May;14(5):259-269. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2018.10. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29472712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Relationship between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Thyroid Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 27;24(19):14605. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914605. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Dysfunction and Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease: A Narrative Review.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025 May 1;16(5):e00828. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000828. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39969015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Value and Thyroid Hormone Variations in Pregnant Women During Pregnancy in Hui'an County in China.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Sep;203(9):4568-4576. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04538-9. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39891831
-
Lipid Hormones at the Intersection of Metabolic Imbalances and Endocrine Disorders.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 18;47(7):565. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070565. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40729034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Pipeline for MASLD: What Can Be Learned from the Successful Story of Resmetirom.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Feb 27;47(3):154. doi: 10.3390/cimb47030154. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40136408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bilirubin Metabolism and Thyroid Cancer: Insights from ALBI and PALBI Indices.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 18;15(7):1042. doi: 10.3390/biom15071042. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianco AC, Salvatore D, Gereben B, Berry MJ, Larsen PR. Biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology, and physiological roles of the iodothyronine selenodeiodinases. Endocr Rev. 2002;23:38–89. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheimer JH, Schwartz HL, Mariash CN, Kinlaw WB, Wong NCW, Freake HC. Advances in our understanding of thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Endocr Rev. 1987;8:288–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

